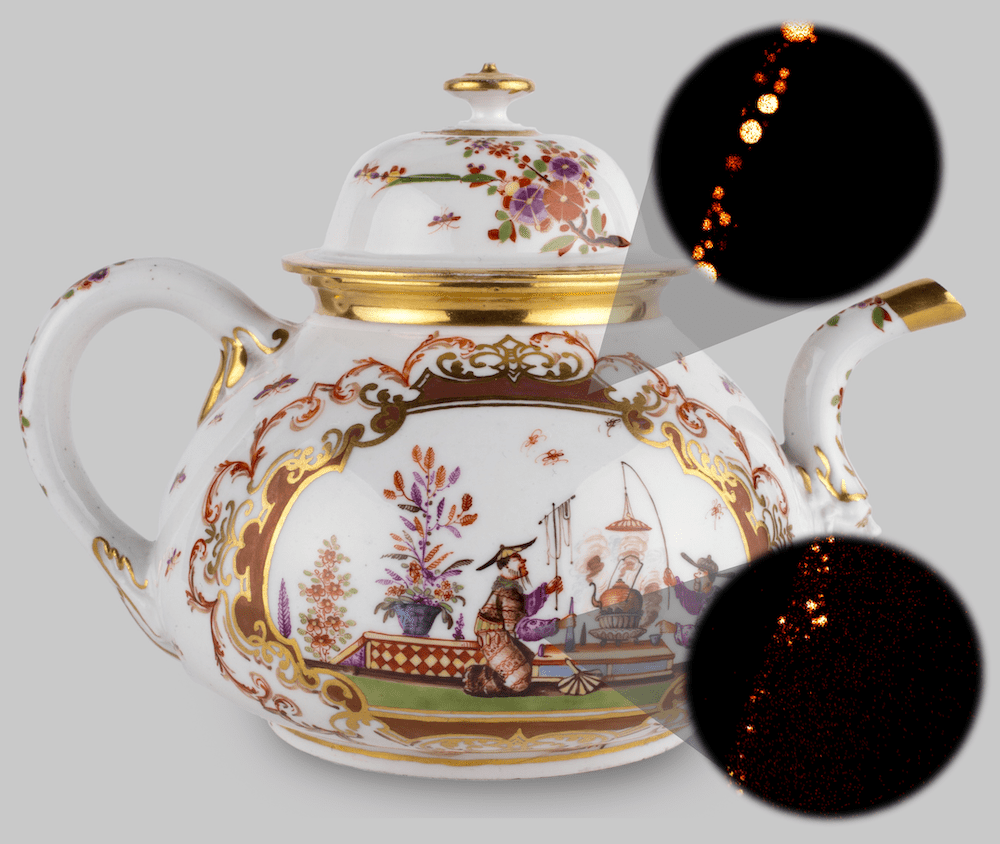
As new analysis methods are developed and refined, researchers can illuminate the science behind past techniques that were designed through trial and error. A group led by researchers from the California Institute of Technology used advanced analytical techniques to show how nanoscale engineering gave a historic purple overglaze its distinctive iridescence.
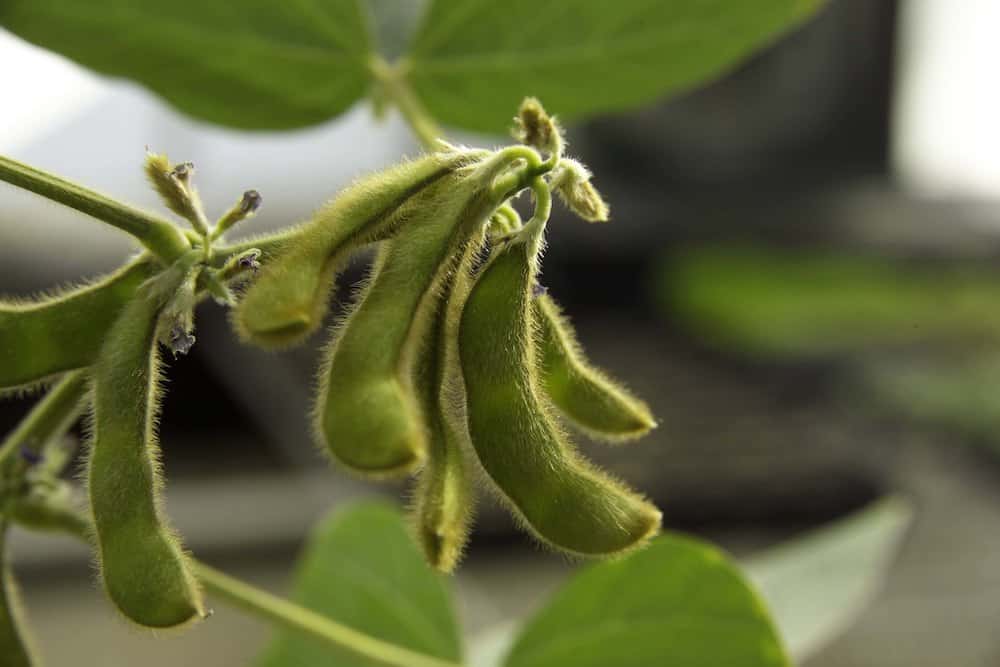
Read MoreThe use of nanotechnology as crop fertilizers is a growing area of interest for farmers. A new study led by Jiangnan University researchers compares the performance of fertilizers based on iron oxide nanomaterials to typical iron chelate fertilizers in promoting soybean growth.
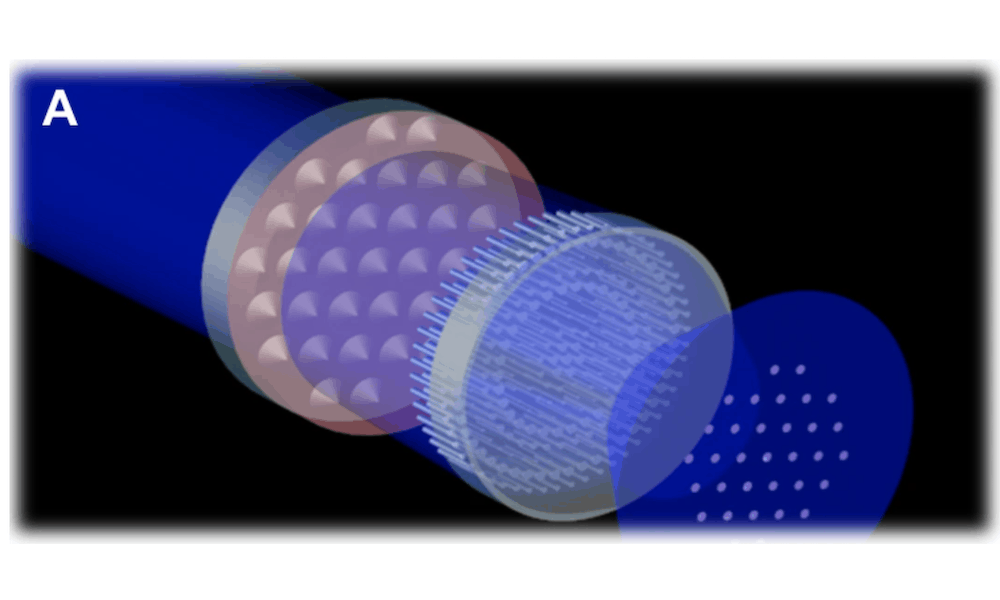
Read MoreInhalable medicine offers several advantages over injections. Researchers in Italy explored the development of inhalable drug-loaded calcium phosphate nanoparticles for treating myocardial cells in the heart.
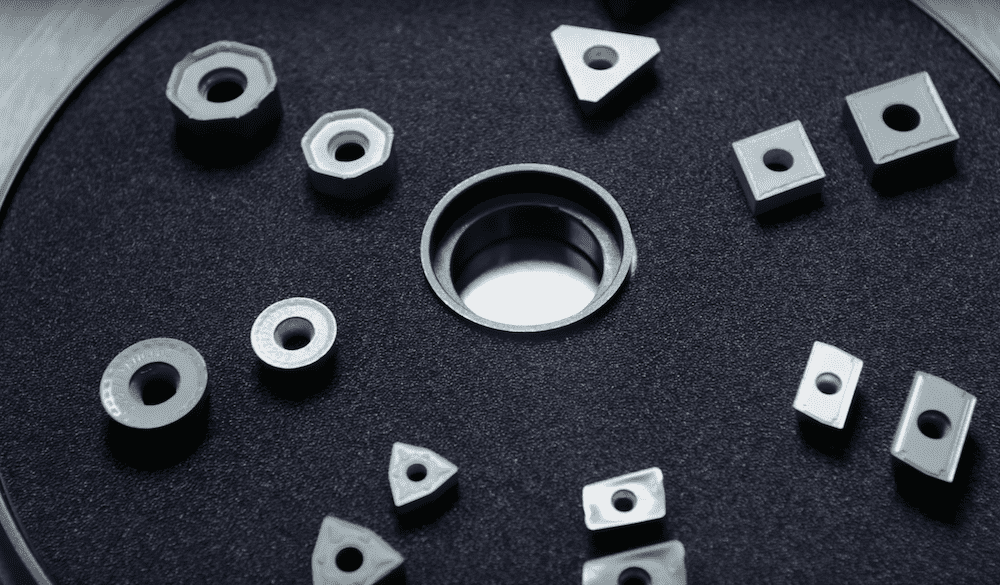
Read MoreCobalt is a main material used as the binder in cemented carbides, but there are drawbacks to using this metal. Ceramic phases have started attracting significant attention as alternative binders, and a recent study dives further into the feasibility of using nanoceramics as a binder.
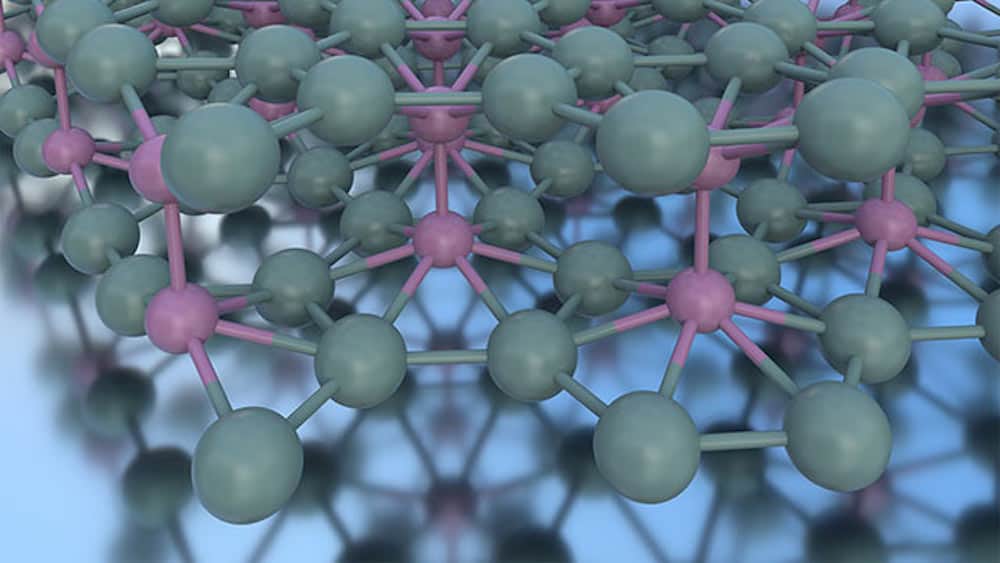
Read MoreThe Hall-Petch relation describes how a ceramic becomes harder as its grains become smaller. But when the grains become small enough, the relation begins to break down. Luis Sotelo Martin and Ricardo Castro of the University of California, Davis, showed that adding extra aluminum to zinc aluminate can extend the Hall-Petch relation.
Read MoreRecent articles on carbon nanotube-containing ceramic composites showed improved properties compared to the original ceramic composite. Two recent articles in ACerS journals demonstrate these improvements.
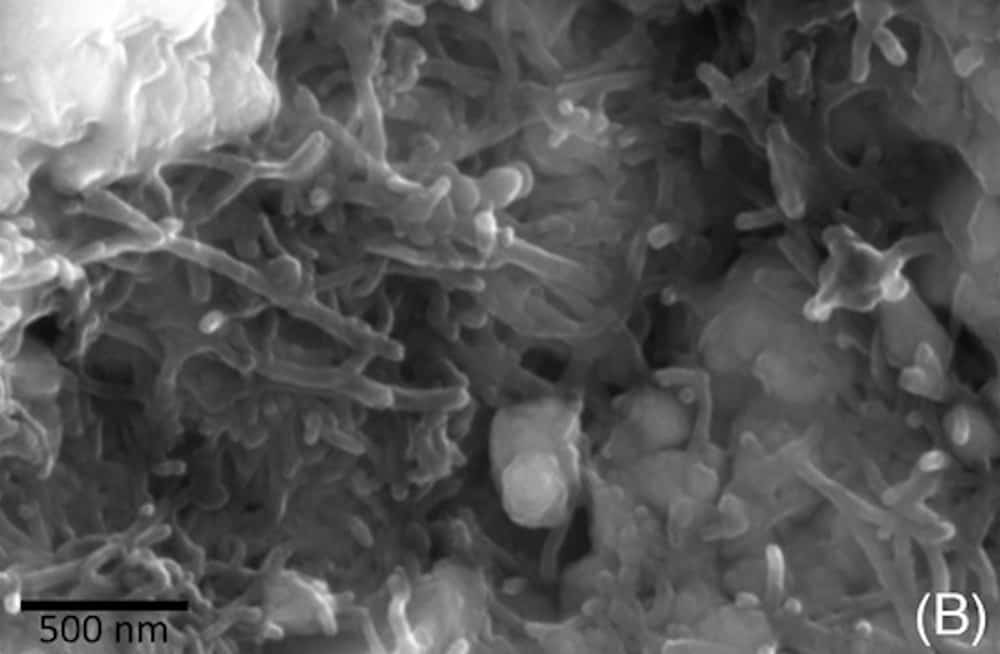
Read MoreSynthesizing multilayer borophene is difficult because of the tendency of boron atoms to cluster. Researchers at Northwestern and Rice Universities discovered they could synthesize bilayer borophene by growing it on a special silver substrate.
Read MoreDeveloping new ways to characterize graphene is essential to developing more rigorous quality standards. Researchers at the University of Adelaide in Australia explored using thermogravimetric analysis to evaluate graphene quality.
Read More