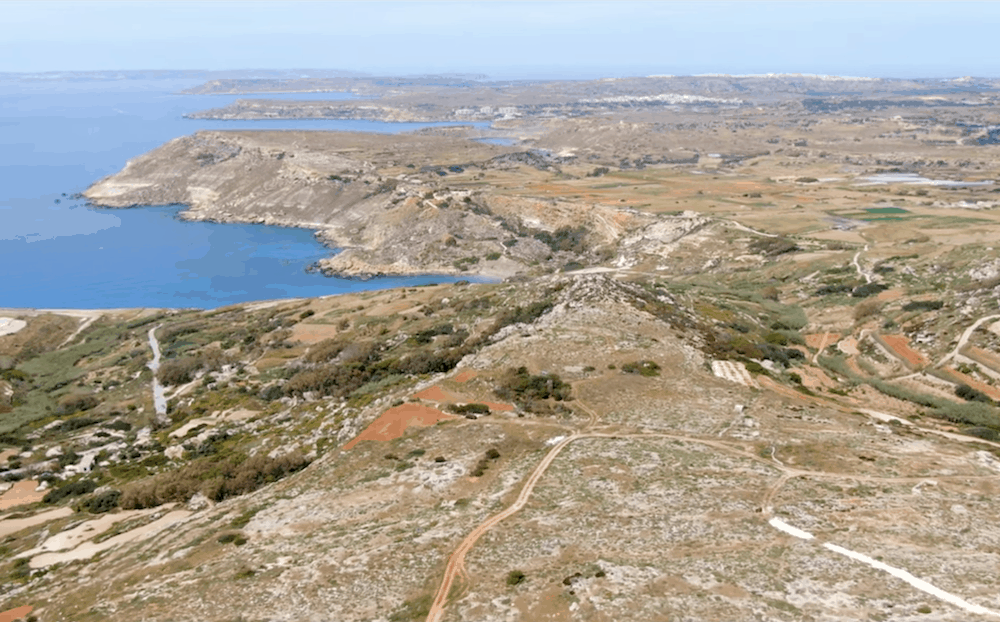
There are relatively few examples of successful recovery and identification of archeological protein residues from ceramic artifacts. Researchers led by the University of Catania in Italy looked to advance the application of proteomics to ancient ceramics by investigating prehistoric pottery from the Maltese Bronze/Iron Age site of il-Qlejgħa tal-Baħrija.
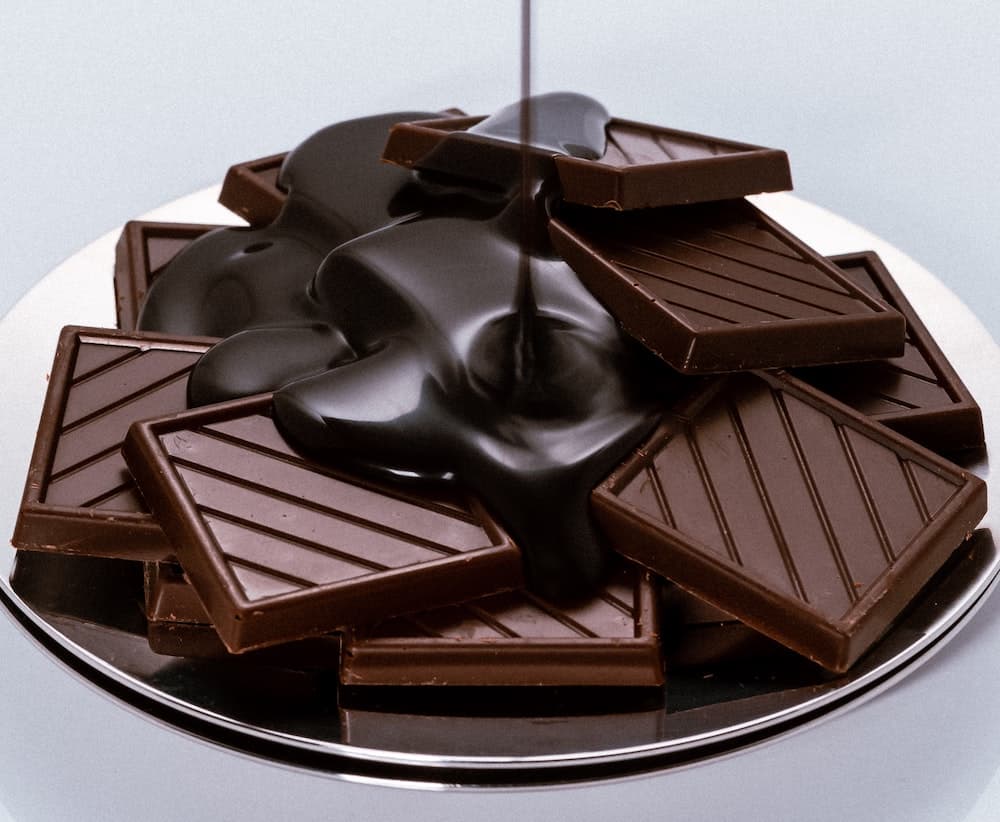
Read MoreProducing chocolate with a shiny, smooth texture and good “snap” requires a complicated heating and cooling process that, on the large scale, is performed using expensive machines. University of Guelph researchers discovered a potentially easier way to achieve the desired texture by modifying the amount of phospholipids in chocolate.
Read MoreDeveloping new ways to characterize graphene is essential to developing more rigorous quality standards. Researchers at the University of Adelaide in Australia explored using thermogravimetric analysis to evaluate graphene quality.
Read MoreMany chemicals are stored in glass containers due to the assumed chemical durability of glass. Purdue University researchers found that glass surfaces can cause some biomolecules to degrade, however—leading them to recommend that these chemicals not be stored in glass containers.
Read MoreThe field of piezoelectric energy harvesting looks to convert mechanical motion, notably from vibration sources, directly into electricity. Recent papers in several ACerS journals discuss challenges and research into developing both materials and processes for PEH.
Read MoreLithium iron phosphate is a widely used cobalt-free cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. It is known to experience certain kinds of defects in its crystal structure, however, and a recent study led by researchers at the Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology explores the existence of hydroxyl groups in phosphorus vacancies.
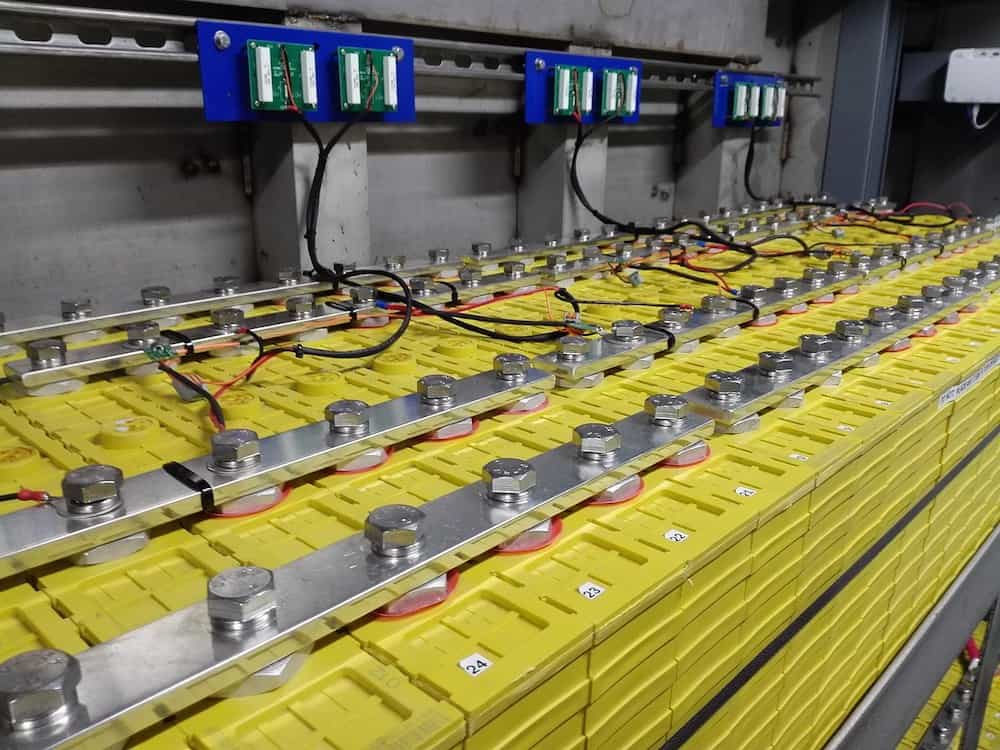
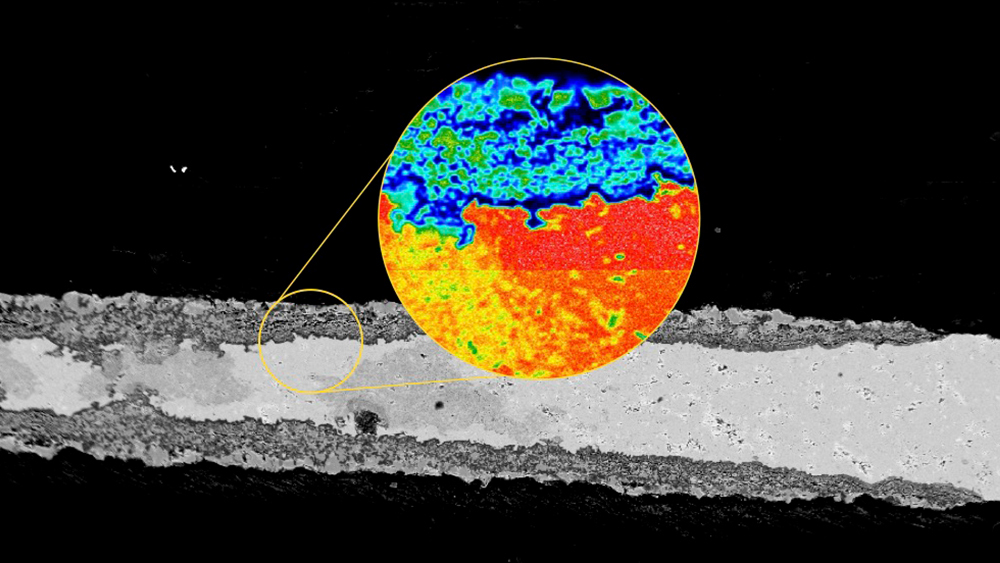
Read MoreOne of the main challenges to commercializing solid-state batteries is stabilizing the interface between the solid electrolyte and electrodes. In a recent paper, researchers from the University of Illinois Urbana–Champaign and Xerion Advanced Battery Corporation look at the role interface morphology and crystallography play in solid-state battery performance.
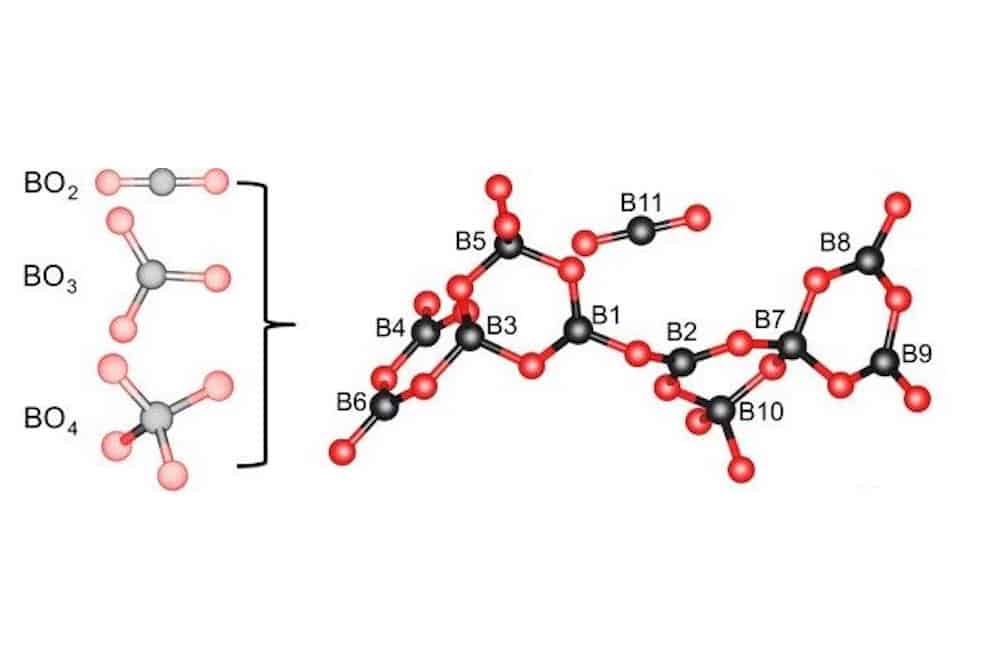
Read MoreCurrent borate-based nonlinear optical materials are reaching the limits of their functionality based on the structural configuration of the borate. A team led by researchers in China and the United States explored arranging borate in the linear BO2 configuration to enhance functionality.
Read MoreDetermining oxidation stability of new MAX phases is a difficult and expensive process with current computational and experimental methods. Researchers at Texas A&M University designed a new machine-learning-based scheme for predicting the oxidation of MAX phases at high temperatures, allowing them to conduct studies that may otherwise take years to perform.
Read More