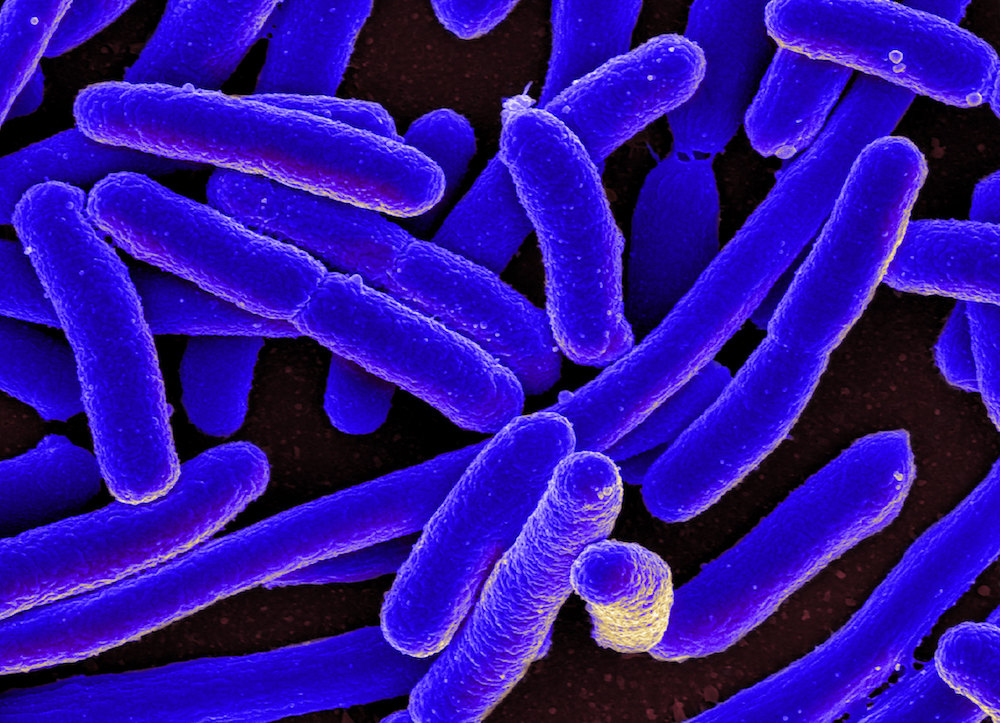
Antibiotic resistant bacteria and antibiotic resistance genes are an increasing concern in water contamination. Rice University researchers are exploring photocatalysis techniques to destroy antibiotic resistance genes, and two papers published this year explore “trap-and-zap” strategies.
Read MoreMid-infrared spectroscopy is an important tool for nondestructive analysis of molecules, but it cannot analyze nanometric volumes very well. One way to improve nanometric analysis is through a technique called nanofocusing, and researchers in Spain and Russia proposed an improved nanofocusing technique using graphene.
Read MoreThere is no shortage of options available when shopping for nonmedical face masks, yet most provide little information about their filter efficiency and breathability—important considerations for a mask that is both efficient and comfortable. But a recent study offers more complete data on the performance of an array of common materials.
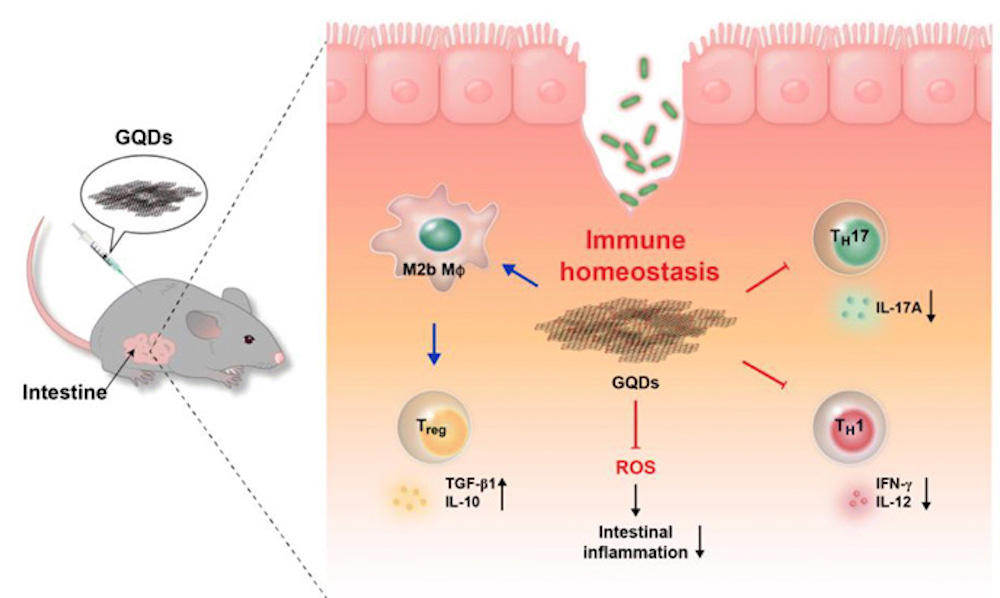
Read MoreTo treat autoimmune diseases, researchers are actively identifying and developing materials that provide control over the immune response. Researchers in Korea found graphene quantum dots may provide an effective treatment for inflammatory bowel diseases.
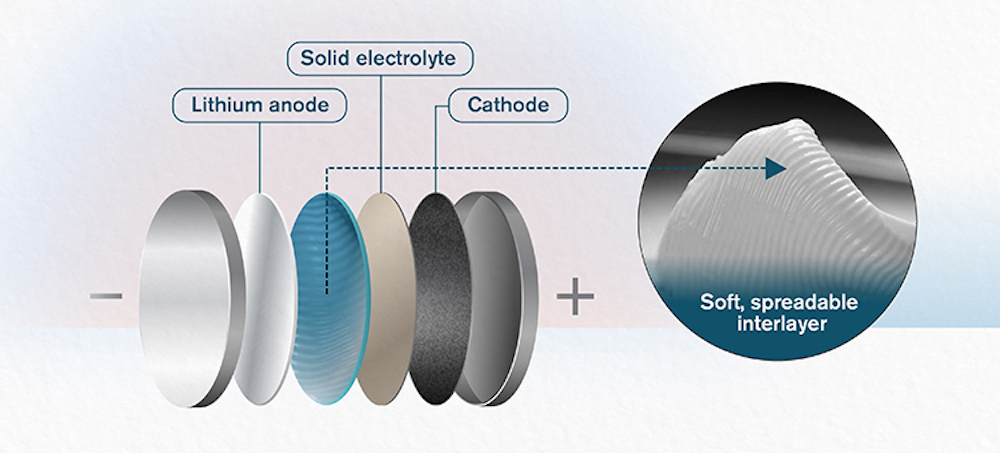
Read MoreScientists at Chalmers University of Technology and Xi’an Jiaotong University developed a new ceramic interlayer—a butter-like mixture of glass-ceramic nanoparticles within an ionic liquid—that provides adequately high ionic conductivity, high thermal stability, and low interfacial resistance to potentially make solid-state batteries a commercial reality.
Read MoreA team of researchers found adding a small amount of graphene can improve the structural alignment of spun carbon fibers, reinforcing their strength—and providing the potential to produce much more inexpensive carbon fiber materials.
Read MoreUnderstanding how nanotubes move in solution is useful for both processing the material and for application in fluid environments, such as the body. Researchers at Rice University investigated how boron nitride nanotubes move in solution and found they behave like rigid rods, just like carbon nanotubes.
Read MoreDefects in a material’s structure offer scientists a way to alter certain material properties. In a new study, three researchers in Russia investigate how different defects in graphene alter the material’s electron transfer kinetics.
Read MoreCeramic nanocontainers, known for their potential as drug carriers in medical applications, are being investigated in a variety of other fields as well. In two recent JACerS articles, George Kordas investigates the potential of ceramic nanocontainers in energy and anticorrosion applications.
Read More