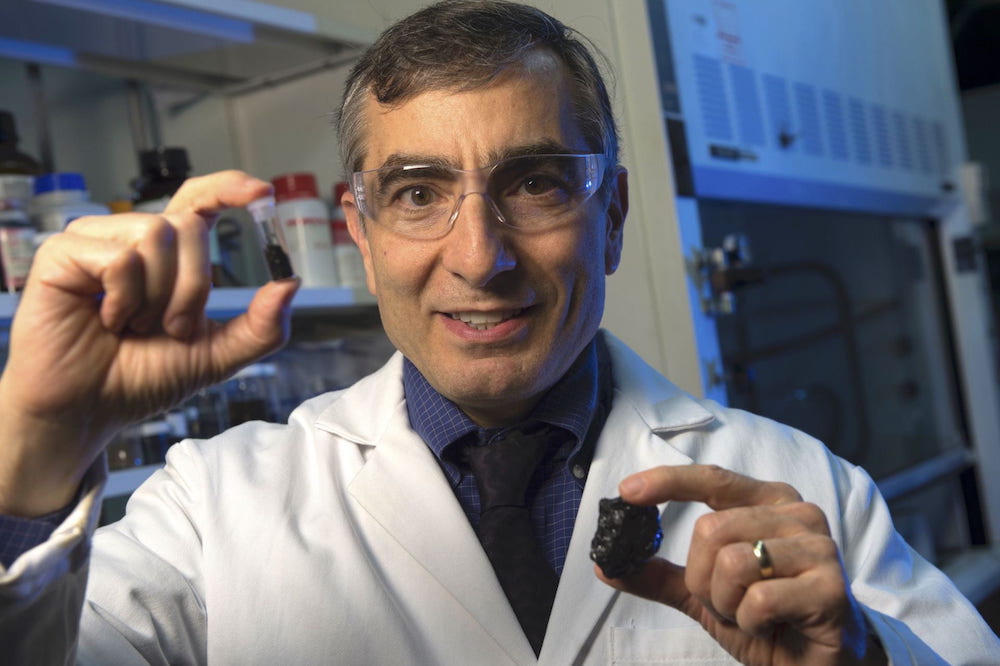
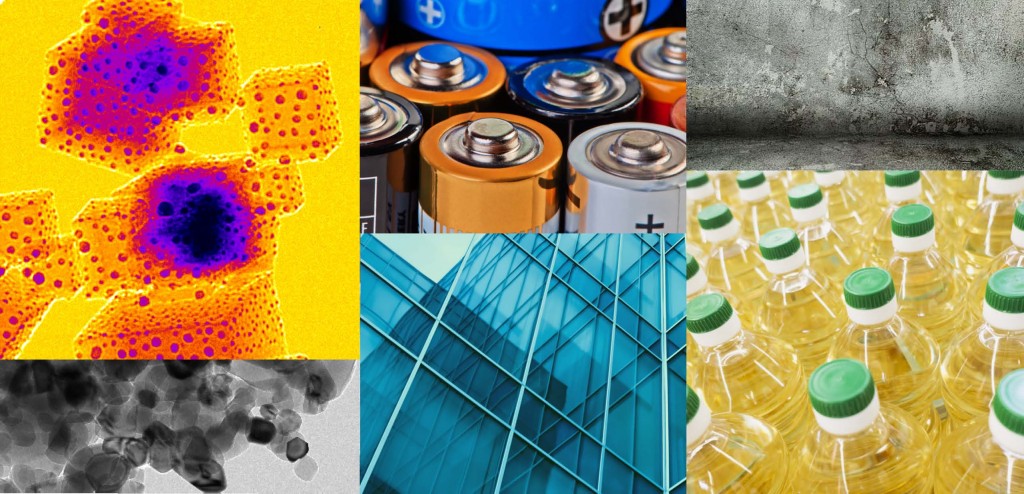
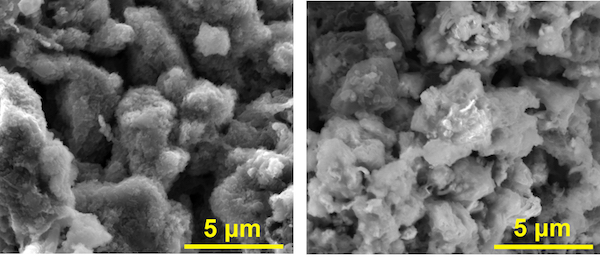
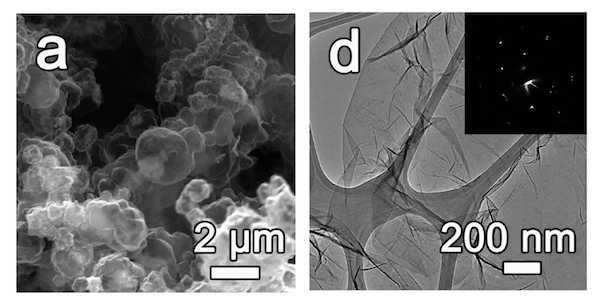
Coal can cause serious health issues when burned as a fuel. But when used as a source of graphene quantum dots, it could help treat traumatic injuries, as Rice University researchers and their colleagues show in new research.
Read MoreResearchers at Rice University in Houston, Texas, have developed a “new form of porous asphalt that can soak up 154% of its weight in carbon dioxide,” according to a university press release.
Read MoreChemists from Rice University in Houston, Texas, are turning up the heat on graphene. They’ve developed a graphene composite material to help heat surfaces and simplify ice removal.
Read MoreScientists are in the fast lane when it comes to driving development of the world’s tiniest super machines. Now engineers are putting their best nanocars on the starting line for the first-ever NanoCar Race, which will be held October 2016 in Toulouse, France.
Read MoreRice University scientists say they have developed a derivative of asphalt—asphalt-porous carbon (A-PC)—that can soak up 114% of its weight in CO2 and is much cheaper than any other carbon capture alternative available.
Read MoreRice University researchers have devised a graphene-laden film that can be applied to glass and plastic to keep their surfaces sans ice, even at frigid temperatures down to –20°C.
Read More