Archive for June 2016
Novel luminescent nanoparticles embedded into glass pave way for high-tech future
In the mission to make glass smarter, researchers at the University of Adelaide in Australia have developed a method for embedding light-emitting nanoparticles into glass without losing any of the nanoparticles’ unique properties.
Read MoreAluminum–cerium alloy has potential to jump-start rare-earth production in the US
A team of scientists from Oak Ridge National Lab, Lawrence Livermore National Lab, and Eck Industries has developed a new super-strong aluminum alloy that incorporates cerium—and it just may be able to restart mining of rare-earth elements in the United States.
Read MoreGraphene could be key to high-efficiency flexible OLEDs in next-gen consumer electronics
Researchers from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) developed what they say is an ideal electrode structure composed of graphene and layers of titanium dioxide and conducting polymers that could lead to highly efficient, flexible consumer electronics.
Read MoreQuantum materials help design longer lasting solid oxide fuel cells
Researchers at Harvard University have devised a different way to generate longer lasting fuel cells, this time using quantum materials.
Read MoreVideo: Improving armor—developing better materials to better protect
When it comes to ceramic materials, body armor is a familiar and favorite topic. But better materials for protecting the lives of those in the line of duty extend beyond ceramics, too.
Read MoreOther materials stories that may be of interest
Graphene electrodes for OLEDs, mantis shrimp inspires ultrastrong materials, and other materials stories that may be of interest for June 8, 2016.
Read MoreGOMD keeps momentum going at Madison, Wis., meeting
More than 360 glass scientists, engineers, and students attended ACerS Glass and Optical Materials Division technical conference and annual business meeting in Madison, Wis., the week of May 22.
Read MoreScientists work towards oxidation-resistant, ultrahigh melting point nanolaminated borides
Researchers from Drexel University (Philadelphia, Pa.), Linkoping University in Sweden, and Imperial College London think that they can make borides better—by giving the material a protective layer of aluminum, the scientists have developed the world’s first corrosion-resistant boride.
Read MoreResearchers look to nature for solutions to ‘greener,’ more sustainable concrete production
Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology are working to identify materials in nature that may be used as inspiration for a sustainable, longer-lasting recipe for cement production.
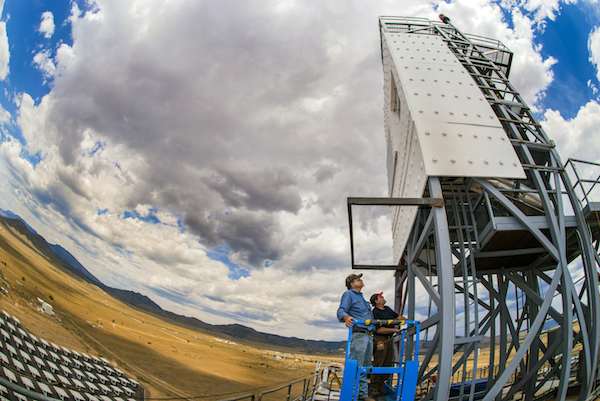
Read MoreTesting shows that Sandia’s falling ceramic particle receiver can still take the heat
Sandia National Lab has completed testing of a novel solar energy storage technique that uses ceramic particles to collect and store the intense heat generated from concentrated sunlight—and the results look promising.
Read More