Posts by Lisa McDonald
Beyond the average: A review of how spatial and temporal structural deviations affect glass-forming oxide systems
Deviations in the atomic structure of glass can significantly affect the material’s macroscopic properties, yet most studies to date do not account for these deviations. A recent review paper led by researchers at The Pennsylvania State University comprehensively reviews various experimental and computational techniques used to characterize and evaluate the effects of these deviations on commercially relevant glass-forming oxide systems.
Read MoreCeramic and glass business news of the week for April 3, 2023
NIST research reactor to restart following two-year shutdown, New York governor announces $2.5 million to support glass waste reduction research, and more ceramic and glass business news of the week for April 3, 2023.
Read MoreThermal properties of cemented carbides: Regression model offers predictions using reliable and readily measurable material characteristics
The accuracy of models for predicting thermal properties of cemented carbides has been limited by dependance on unreliable conductivity data or time-consuming grain size measurements. Two researchers at a Sweden-based tooling company formulated a regression model that offers fairly accurate predictions using only reliable and readily measurable material characteristics.
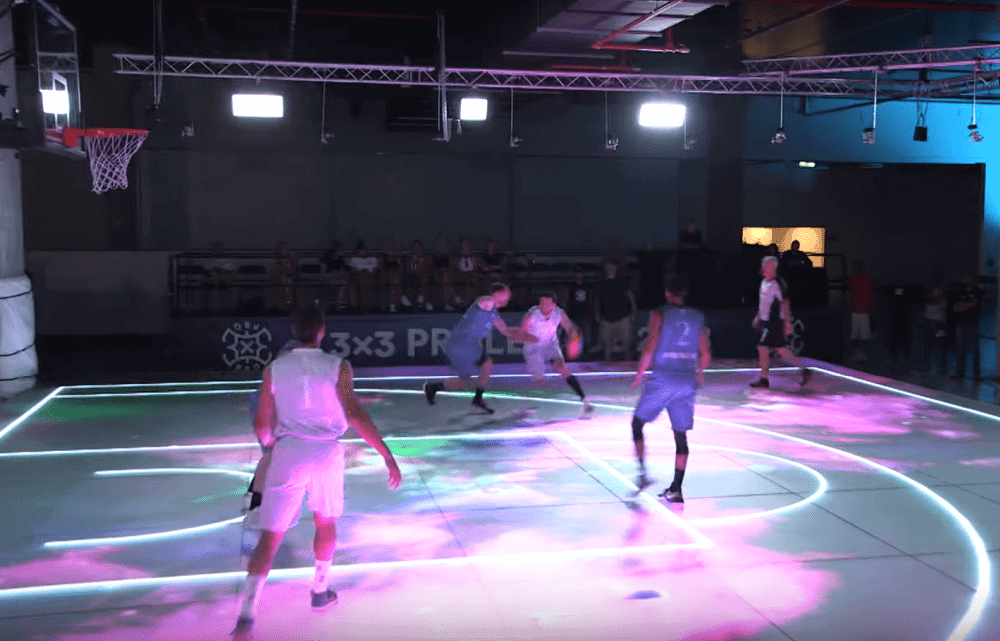
Read MoreVideo: Glass court to debut on world stage during FIBA U19 Women’s Basketball World Cup
Advancements in glass processing and design have improved the material’s mechanical properties to the point that glass is starting to be used in load-bearing applications. In July 2023, the use of a novel glass court will debut on the world stage during the FIBA U19 Women’s Basketball World Cup.
Read MoreOther materials stories that may be of interest for March 29, 2023
Oxygen-ion battery, zap ‘forever chemicals’ for good, and other materials stories that may be of interest for March 29, 2023.
Read MoreNew solid-state NMR strategy cracks open the ‘black box’ of crystal nucleation in glass
The process by which a crystal nucleates and grows within a glass during heat treatments remains a conceptually ill-understood phenomenon. Researchers in Brazil developed a nuclear magnetic resonance strategy combined with atomistic computer simulations that allowed them to shed unprecedented light on the structural changes that take place in a glass during relaxation and crystal nucleation.
Read MoreCeramic and glass business news of the week for March 27, 2023
U.S. and Indonesia announce partnership on SMRs, U.S. Treasury to release EV battery sourcing rules, and more ceramic and glass business news of the week for March 27, 2023.
Read MoreLow-carbon cement technology heading from lab to market
The recent one-year anniversary of the National Science Foundation’s Directorate for Technology, Innovation, and Partnerships is a reminder of the federal government’s commitment to take a larger role in supporting the transition of use-inspired research from the lab to the marketplace. Ideally this support will allow more university researchers to follow in the footsteps of Sublime Systems, a spinout from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology that aims to commercialize a low-carbon cement technology.
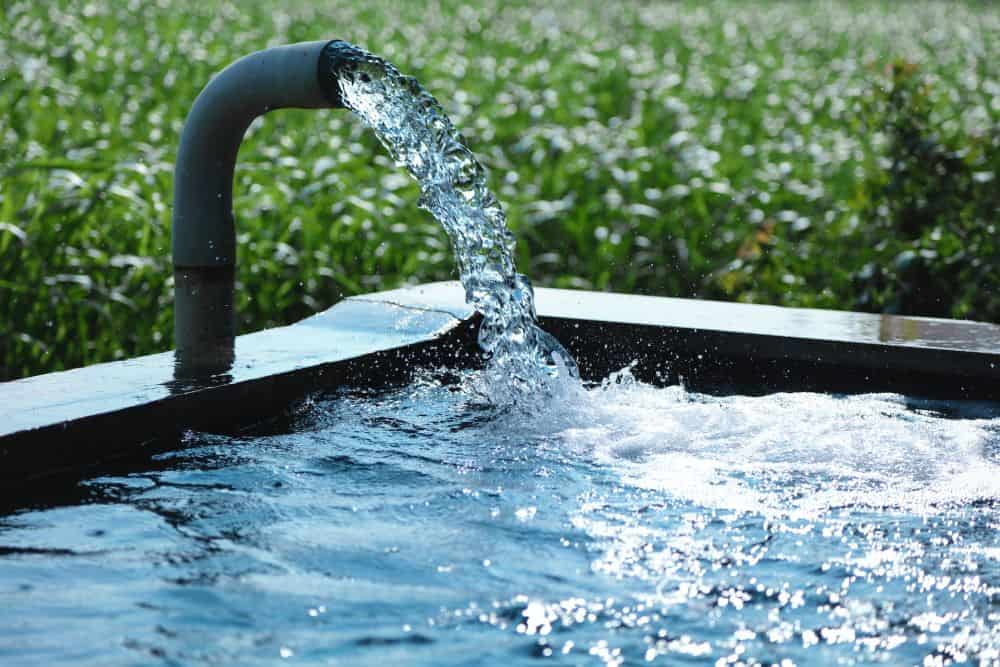
Read MoreVideo: World Water Day 2023—how ceramics and glass accelerate change to solve the water and sanitation crisis
This year’s World Water Day on March 22 focuses on accelerating change to solve the water and sanitation crisis. Today’s CTT is a collection of articles from the past year that illustrate how ceramic and glass materials support this goal.
Read MoreOther materials stories that may be of interest for March 22, 2023
Sustainable plastics upcycling, stronger concrete, and other materials stories that may be of interest for March 22, 2023.
Read More