The effect niobium oxide has on the macroscopic properties of glass is reasonably well-known, but its specific structural role in glass remains poorly understood. To address this knowledge gap, researchers from the Center for Research, Technology, and Education in Vitreous Materials in Brazil combined spectroscopic data on niobium-containing silicate glasses with advanced computational modeling.
Read MoreCeramics and glass are often considered to be inert materials, but such stability is not always the case. Researchers in Japan demonstrated that certain ceramic glazes could potentially degrade the catechins found in tea under specific laboratory conditions, though future studies would need to confirm the results in a more realistic setting.
Read MoreEvaluating the quality of research and researchers is neither easy nor simple. An open-access paper by two ACerS journal editors demonstrates how some newer evaluation methods can better capture the short- and long-term performance of journal articles.
Read MoreInitially proposed as a simple pondering by a U.S. chemist in the 1940s, the controversial Kauzmann paradox has inspired hundreds of follow-up papers in a variety of scientific disciplines. Now, researchers in the U.S. and Brazil led by ACerS Fellows Edgar D. Zanotto and John C. Mauro argue it may be best to focus future glass research elsewhere.
Read MoreGroup-III-nitride semiconductors have considerable potential for electronic and optoelectronic applications, but unintended defects tend to form in their structure during fabrication, which may affect the electrical properties. Two researchers at the University of British Columbia detailed the striking contrast between the effects of threading dislocation lines in gallium nitride versus indium nitride.
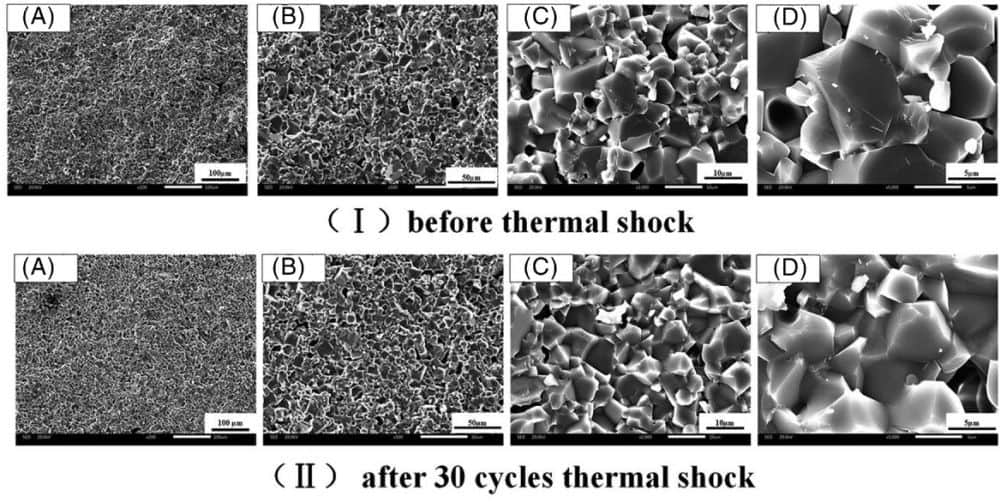
Read MoreStarting materials can often be derived from different sources, but the impact that material source has on a product’s properties is generally less studied than other factors, such as synthesis technique. Researchers from Wuhan University of Technology explored the effect of different magnesium sources on the production of magnesium aluminate spinel.
Read MoreThough the presence of water on the moon is a well-confirmed fact, the origins of this water and its distribution on the lunar surface remain largely unknown. Thanks to new lunar samples brought back by the Chinese Chang’e 5 lunar exploration mission, researchers now know that impact glass beads appear to play a significant role in the lunar surface water cycle.
Read MoreFerroelectricity traditionally is believed to only occur in compounds. However, in the past decade, some theoretical works suggested that ferroelectricity is possible in certain elementary substances. Now researchers in China and Singapore experimentally confirmed ferroelectricity in monolayer α-phase bismuth.
Read MoreAll known piezoelectric materials to date are solids. But a shocking discovery at Michigan State University turns this conventional wisdom on its head. They observed the piezoelectric effect in two room-temperature ionic liquids, and this discovery could necessitate a modification of current piezoelectric theory.
Read MoreDeviations in the atomic structure of glass can significantly affect the material’s macroscopic properties, yet most studies to date do not account for these deviations. A recent review paper led by researchers at The Pennsylvania State University comprehensively reviews various experimental and computational techniques used to characterize and evaluate the effects of these deviations on commercially relevant glass-forming oxide systems.
Read More