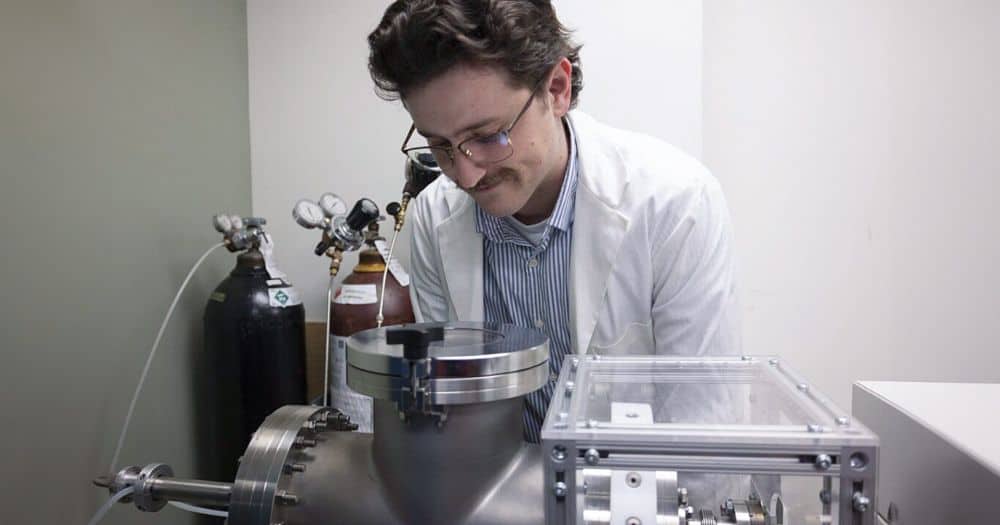
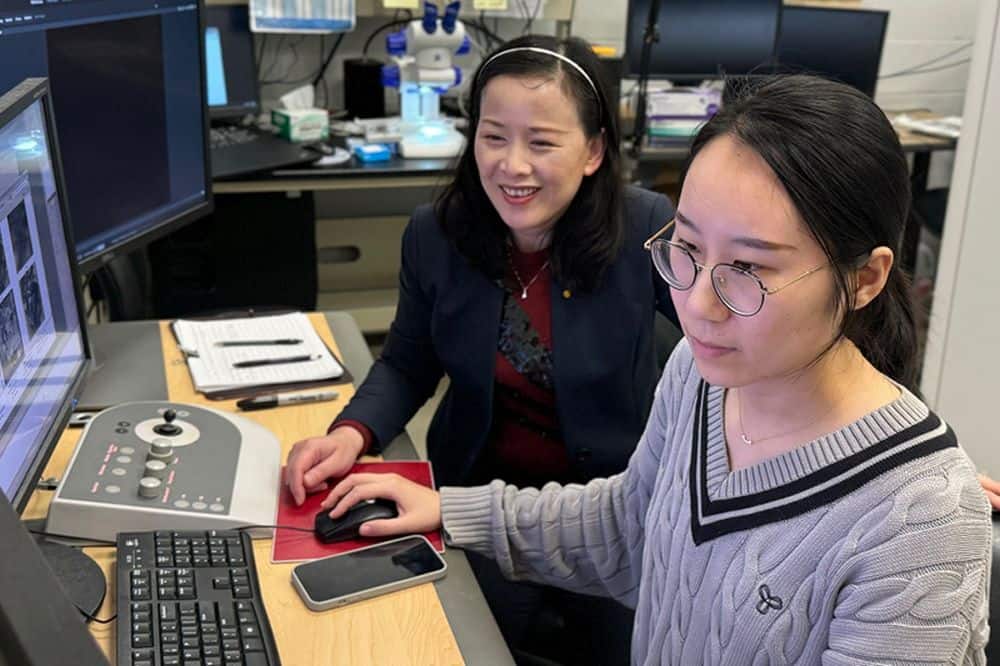
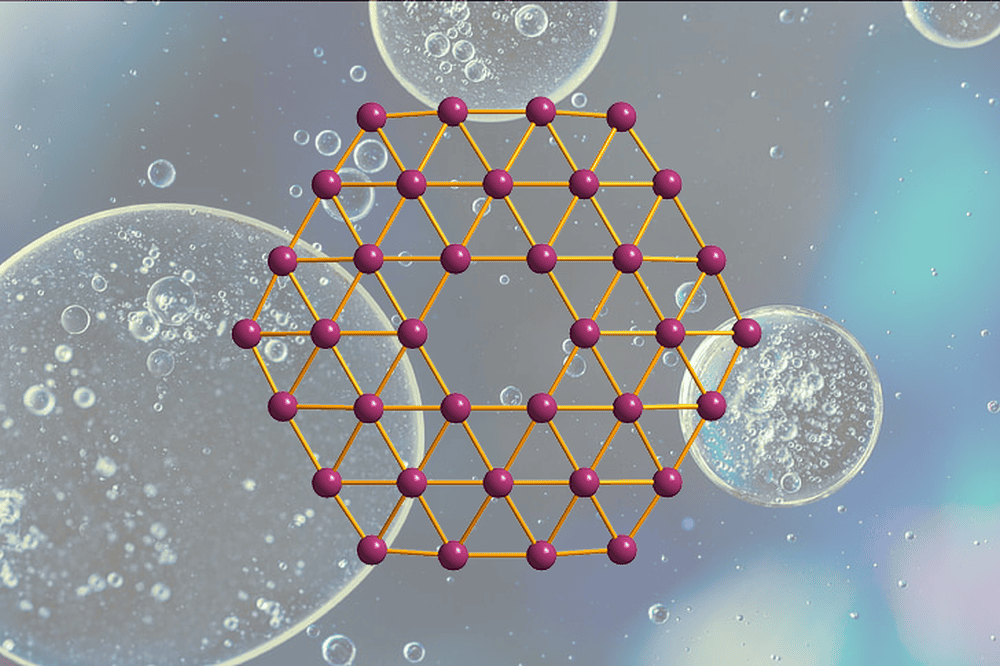
In a new record for auxetic materials, researchers at the University of Western Ontario synthesized 2D flakes of tungsten semicarbide than can expand up to 40% under applied strain.
Read MoreBorophene, a relatively new nanomaterial, is beginning to make its way into biomedical applications. Researchers at The Pennsylvania State University showed that synthesizing borophene with chiral structures allows it to interact with mammalian cells in distinct ways.
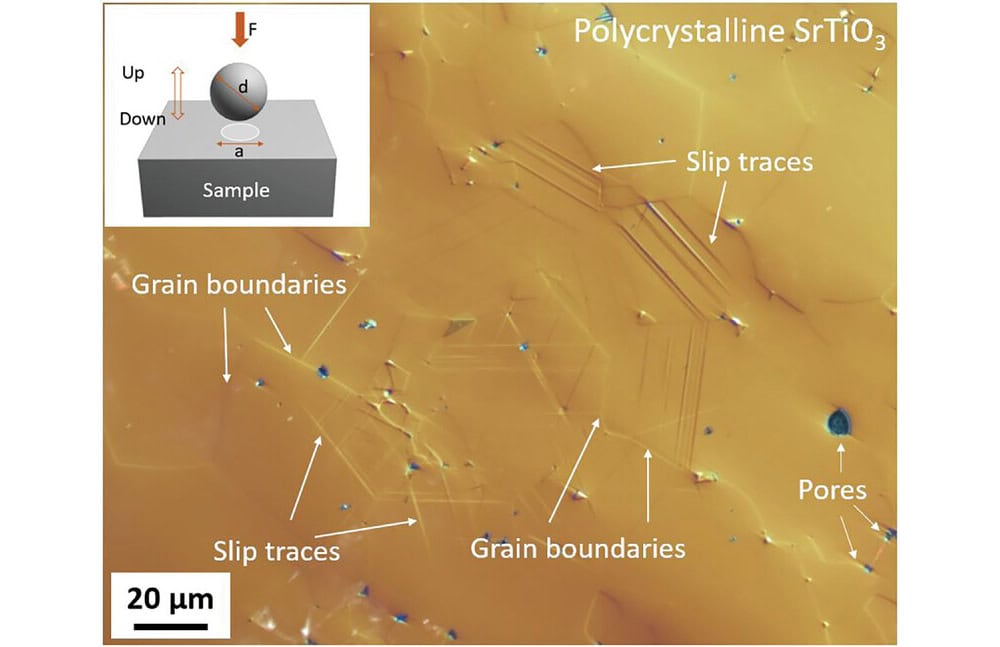
Read MorePlastic deformation of polycrystalline ceramics at room temperature is hindered by the lack of sufficient independent slip systems within the material’s structure. Researchers in Germany circumvented this limitation by focusing on deformation in the near-surface region, which demonstrates several useful dislocation mechanisms not available in the bulk region.
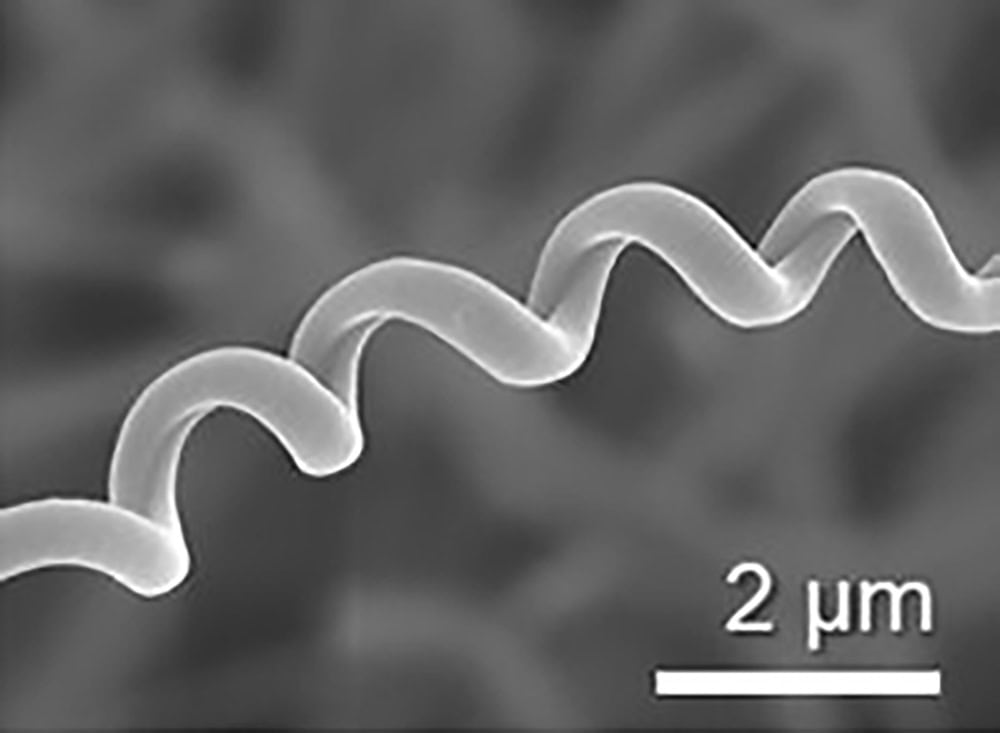
Read MoreConventional electrospinning of sol–gel ceramic solutions places limitations on the composition and structural integrity of the resulting fiber. University of Oxford researchers showed that uniform, flexible ceramic nanofibers and springs can be created using the modified technique of coaxial electrospinning.
Read MoreThe June/July 2024 issue of the ACerS Bulletin—featuring a look at novel materials and architectures for digital technologies—is now available online. Plus—“Emerging Professionals” section and C&GM.
Read MoreDrawing inspiration from the structure of existing pigments, Oregon State University researchers developed a new magenta pigment based on divalent chromium, which could be a promising chromophore for a rainbow of new inorganic colors.
Read MoreThe growing field of dislocations in ceramics paves the way to harness versatile, unexpected functional and mechanical properties. Recent papers provide a roadmap for this emerging field and describe a new method for engineering dislocations that may work in industrial settings.
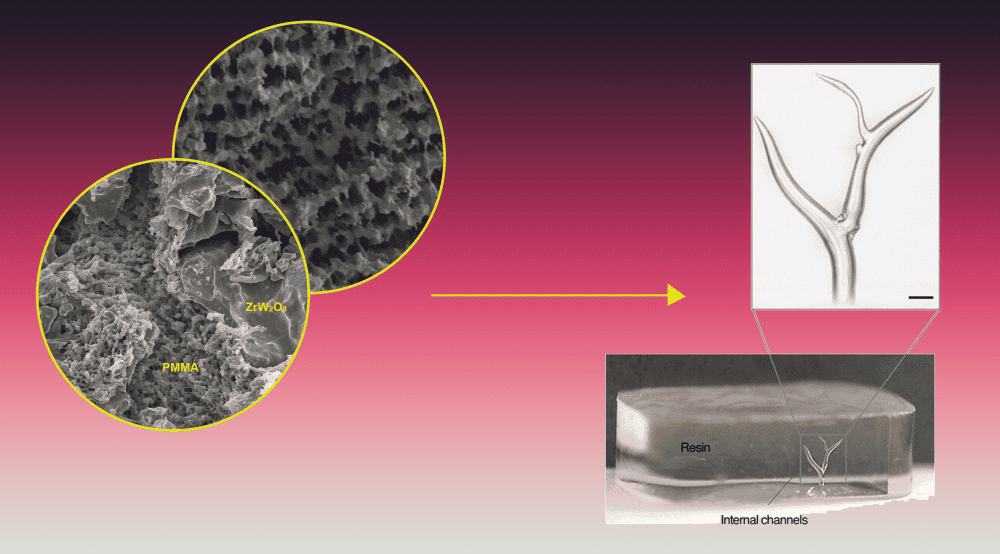
Read MoreAdvancements in the ceramics field have often supported innovation and discoveries in other fields. Now, knowledge gained from early work on ice-templated ceramics is aiding in the development of soft, bioinspired materials for medical applications.
Read More