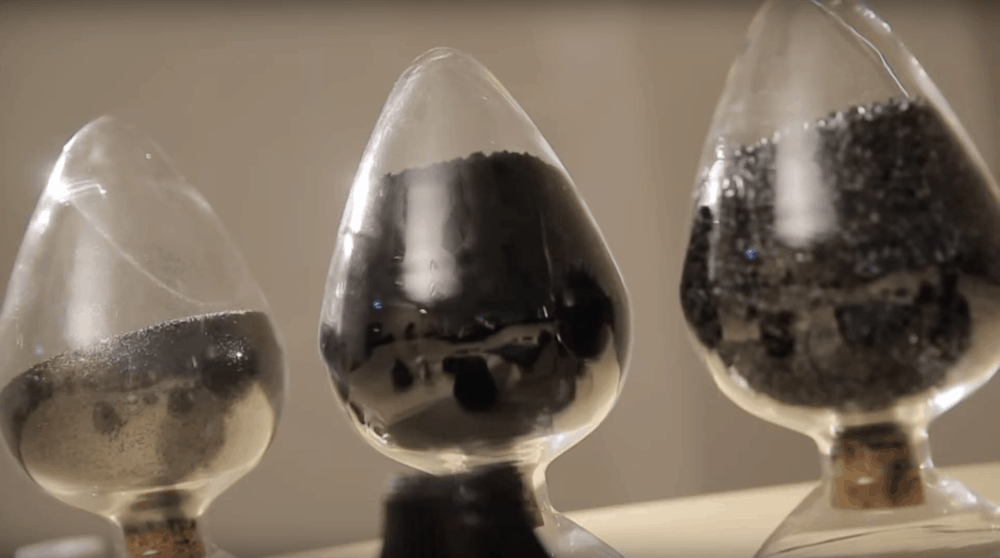
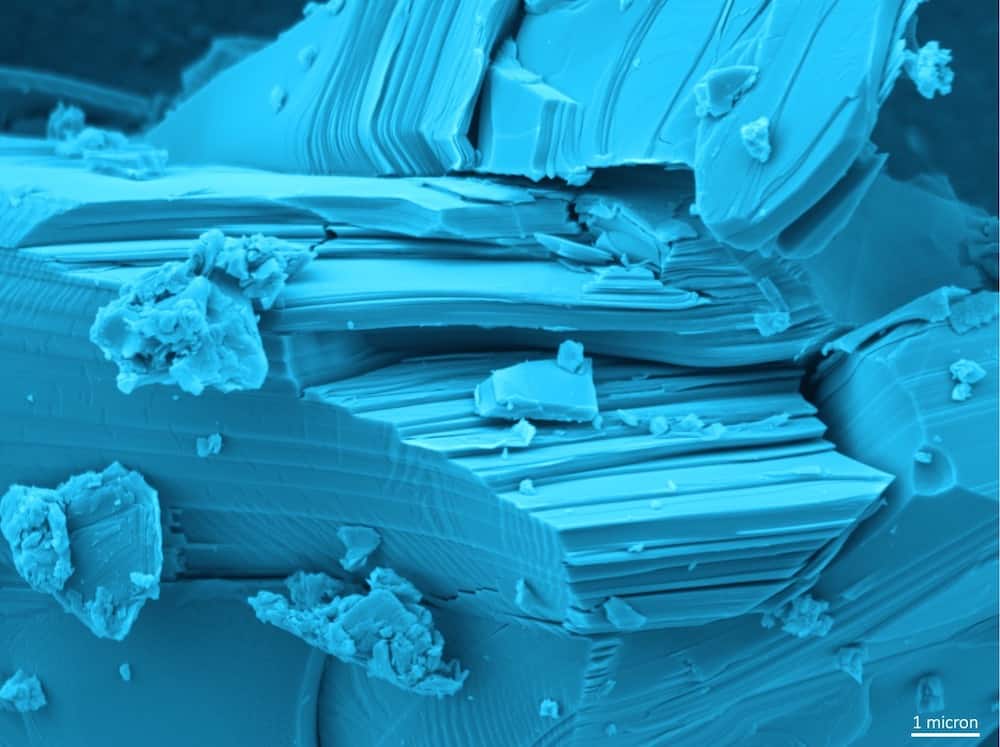
Developing new ways to characterize graphene is essential to developing more rigorous quality standards. Researchers at the University of Adelaide in Australia explored using thermogravimetric analysis to evaluate graphene quality.
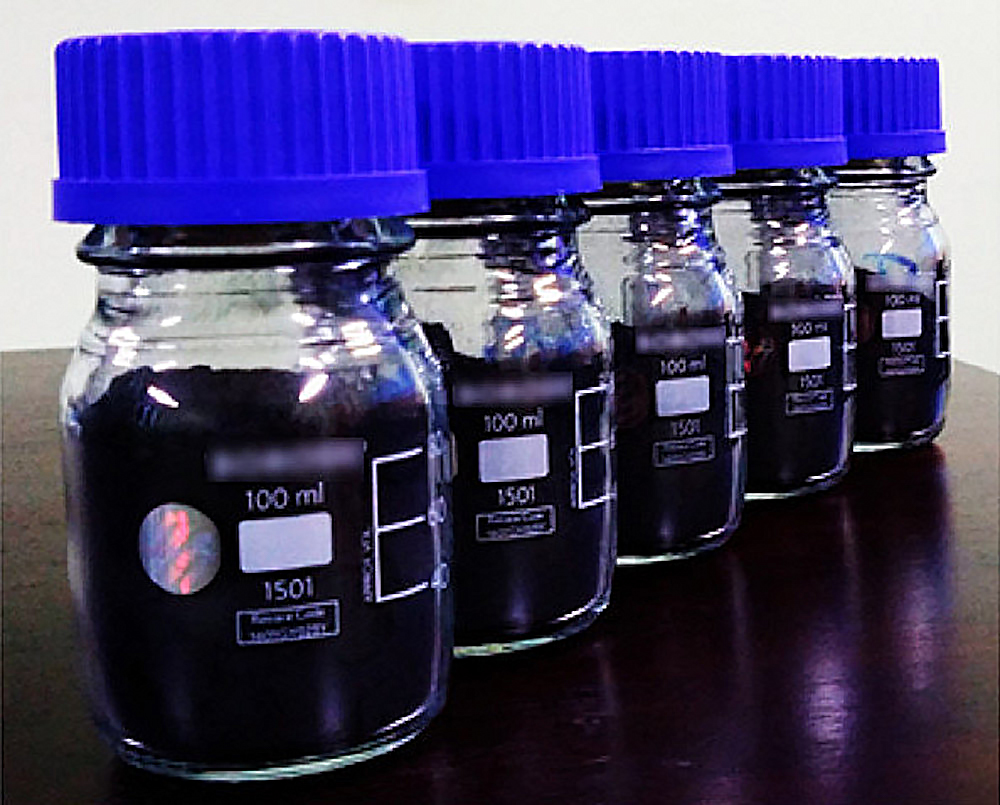
Read MoreDespite the extensive number of studies on high-entropy 3D crystalline solids, very little has been reported on high-entropy 2D materials. Researchers led by Indiana University–Purdue University Indianapolis demonstrated the opportunities for creating high-entropy 2D materials using MXenes.
Read MorePeriprosthetic joint infection is a serious complication that can occur in joint replacement surgery. Researchers in Italy and the United States review the research on using nanotechnology to prevent and treat PJI.
Read MoreMXenes, the family of 2D transition metal carbides and nitrides, was first discovered in 2011. To celebrate the 10th anniversary of this discovery, researchers led by Drexel University professor and ACerS Fellow Yury Gogotsi published a forward-looking review article in Science that explores the impact and promise of this material family.
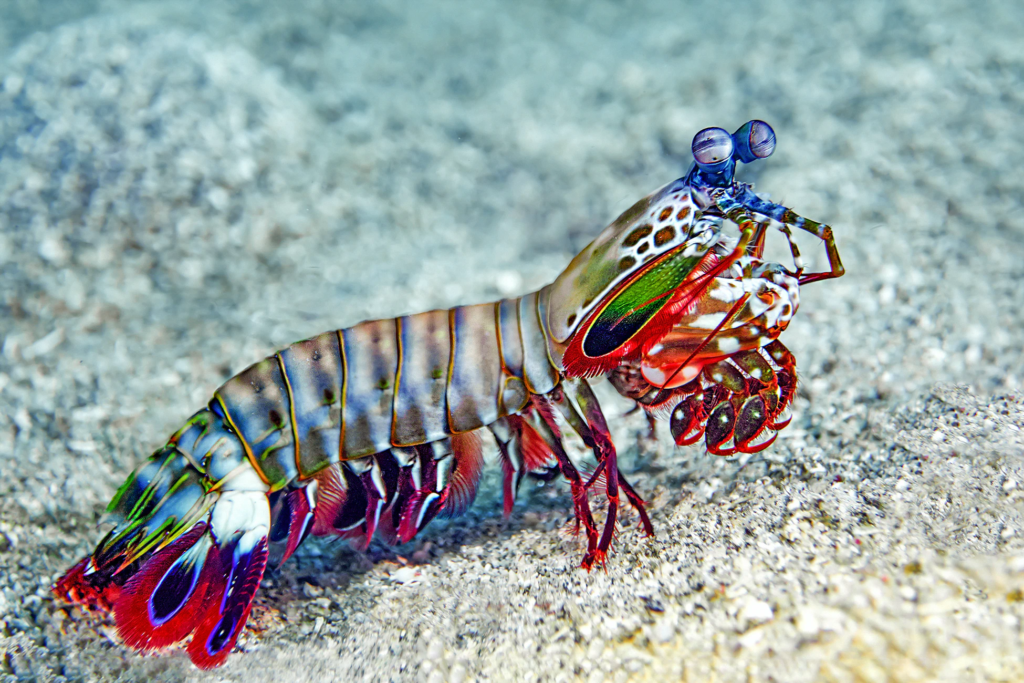
Read MoreArtists and scientists alike find inspiration in nature. But two recent scientific studies found inspiration in the same creature: the mantis shrimp. The creature’s incredibly tough materials and complex eyes inspired innovations that could lead to fracture-resistant biocomposites and highly advanced optical sensors.
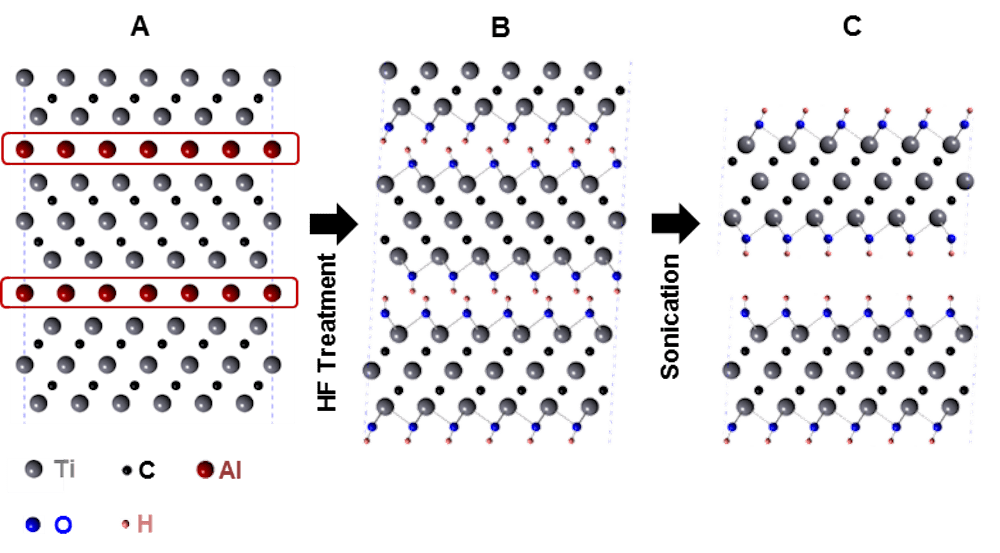
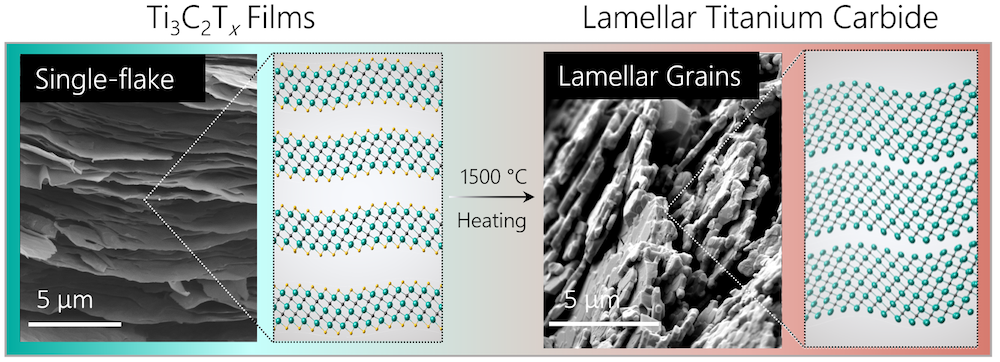
Read MoreMXenes hold potential as additives in ultrahigh-temperature ceramics to improve mechanical properties—but a gap in understanding the phase stability and transformation of MXenes at high temperatures limits this application. Researchers at Indiana University–Purdue University Indianapolis investigated these properties in titanium carbide MXenes.
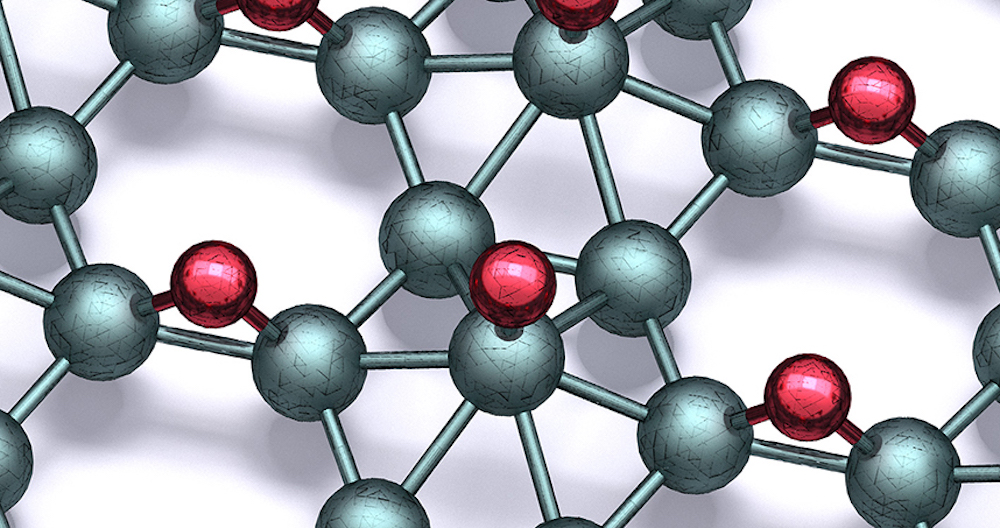
Read MoreThe 2D material borophene holds a lot of potential due to its flexibility, strength, and diverse atomic structure—but rapid oxidation of borophene in air makes application difficult. Researchers led by Northwestern University experimentally investigated the hydrogenation of borophene to see how well it stabilizes the material for practical use.
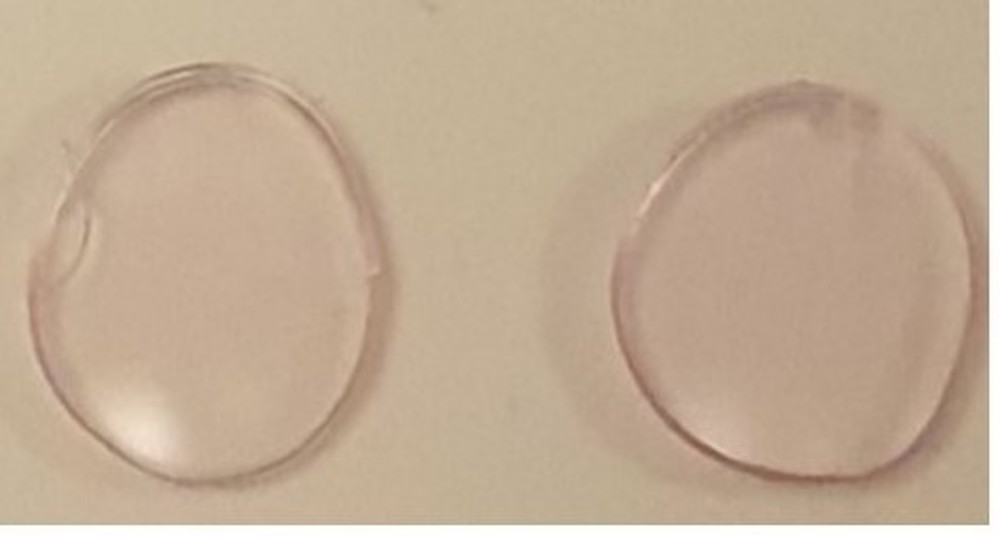
Read MorePeople who have color vision deficiency see colors differently from others. Tinted glasses and contact lenses offer a way to manage the condition, but to date only the former option is reliably effective. Researchers developed a new type of tinted contact lens using gold nanoparticles that shows potential for commercial scale-up.
Read MoreCurrent methods of graphene production face tradeoffs among speed, cost, and material quality. Researchers from the Indian Institute of Technology Patna propose a new method based on plasma spraying that may offer the best outcome for all of these factors.
Read More