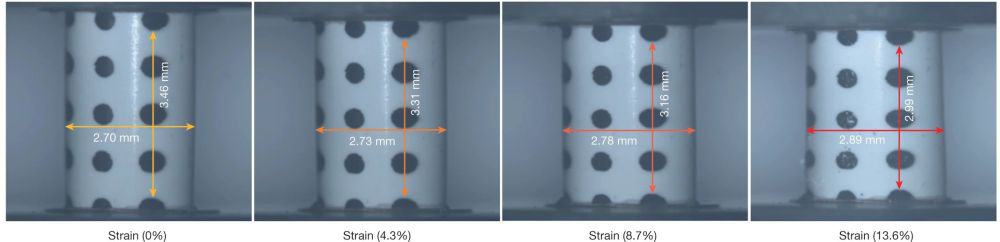
Successful plastic deformation of nitride ceramics has to date been limited to samples on the micro and nanoscale. Now, researchers from Yanshan University in China achieved plastic deformation in a bulk boron nitride ceramic by modifying its layered van der Waals structure.
Read MoreResearchers in Japan showed that adhesive tape, though not the answer to mass graphene production, may be an ideal solution for mass transfer of 2D materials.
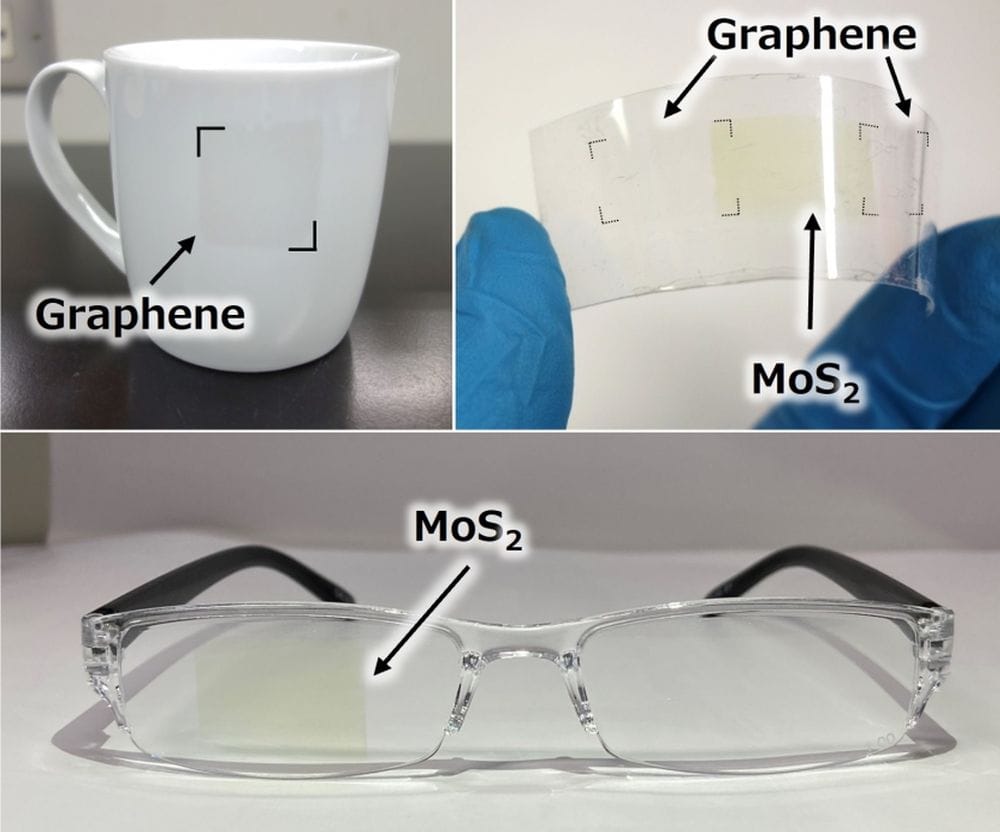
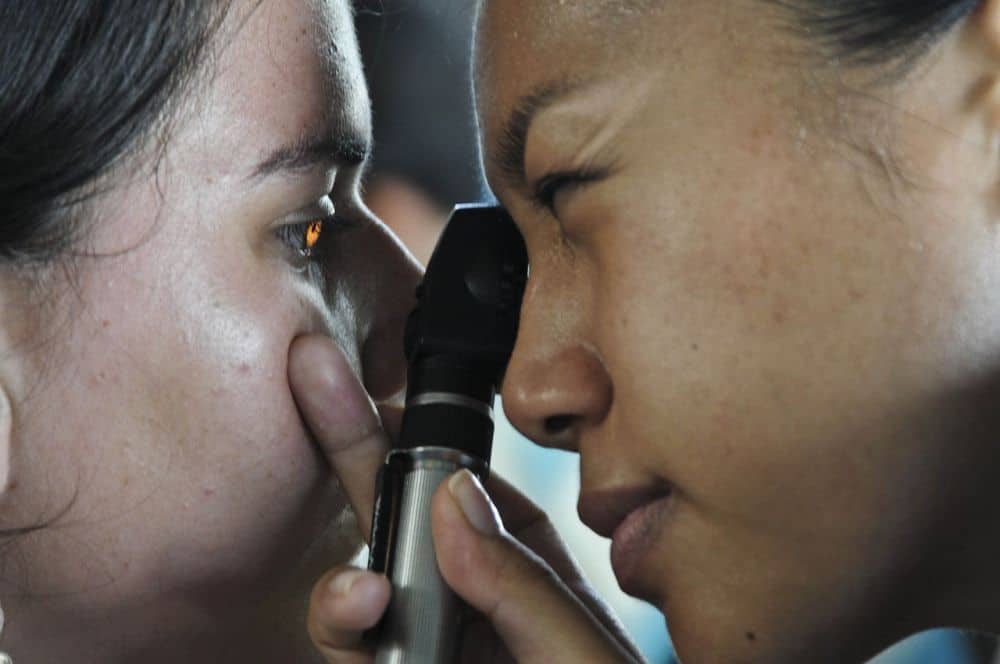
Read MoreTo date, efforts to develop retinal prostheses have achieved limited success. But the turn toward flexible rather than rigid platforms for these devices is leading to significant advances in the research community.
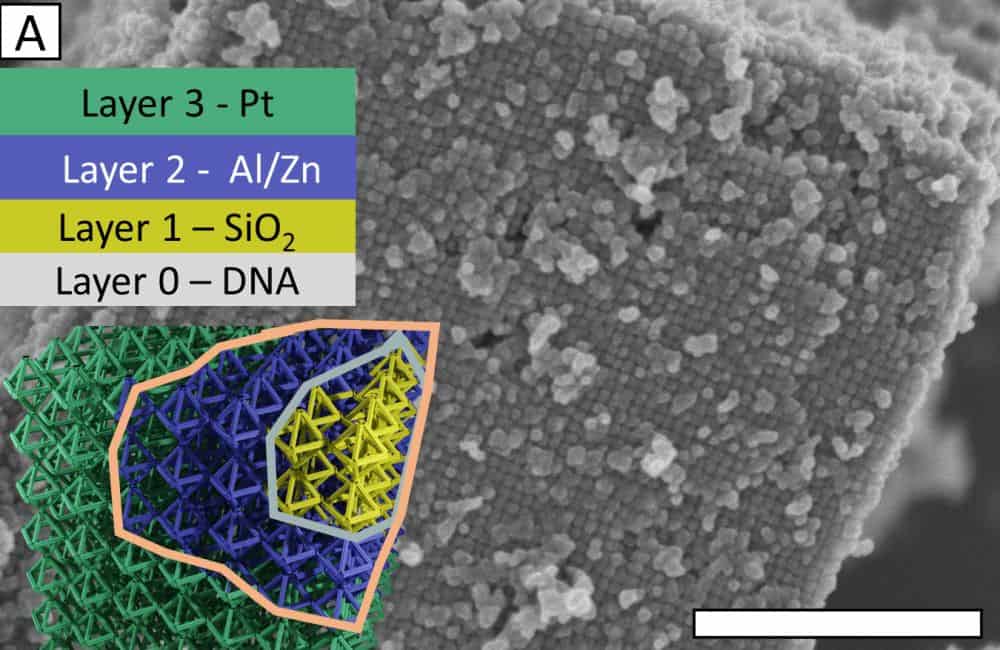
Read MoreIn July 2023, researchers announced the creation of high-strength, lightweight glass nanolattices by coating DNA origami scaffolds with silica. Their new open-access paper, published in January 2024, describes the functionalization of these glass-coated scaffolds by infiltrating the nanolattice with metal and metal oxide particles.
Read MoreElectrocaloric materials have potential to replace liquid refrigerant in cooling systems, thus avoiding the emission of harmful greenhouse gases. But currently, electrocaloric devices can only operate within a small temperature span. A recent study reported a new electrocaloric prototype with greatly improved temperature span and cooling power.
Read MoreDuring CES 2024, which took place January 9–12 at the Las Vegas Convention Center, numerous companies showcased solar technology innovations. Today’s CTT highlights several key announcements made during the show.
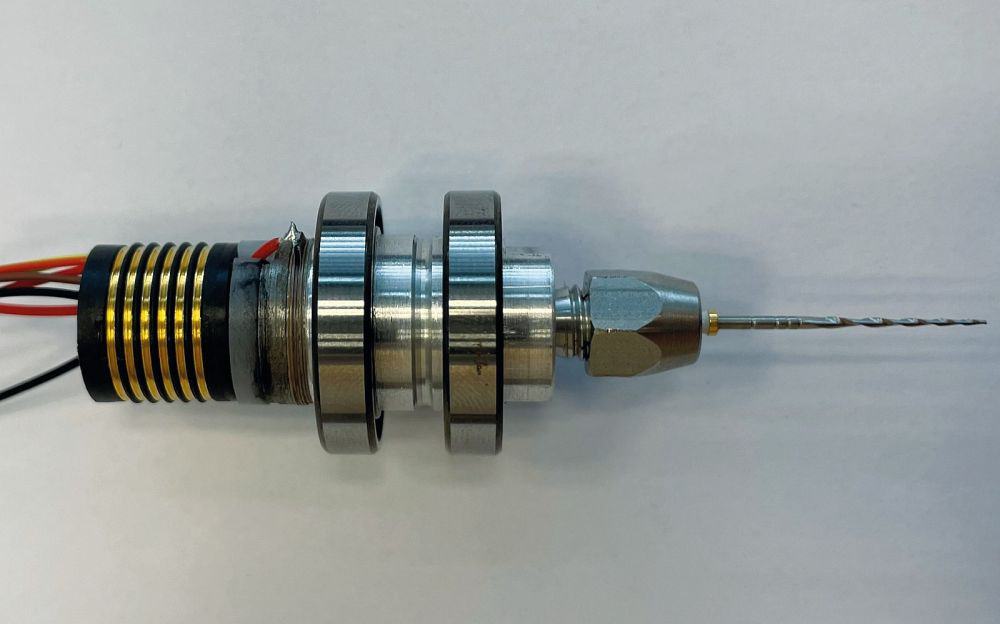
Read MoreThough modern root canal treatments are not overly painful thanks to advancements in medical technology, the need to frequently clean the rotary file can lengthen procedure time. Researchers at Fraunhofer Institute for Ceramic Technologies and Systems IKTS created a file that features both rotational and vibrational motion, which reduces the amount of cleaning required.
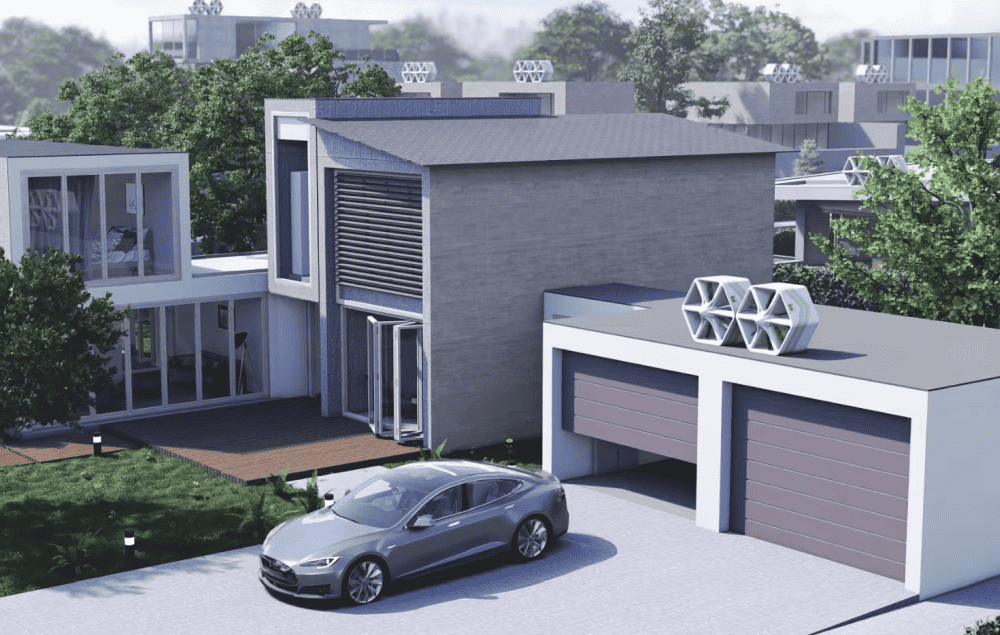
Read MoreThe large size of traditional wind turbines can make transportation and installation of these devices difficult in certain locations. Scottish technology startup Katrick Technologies designed a honeycomb-shaped wind generator that can be easily installed in urban settings.
Read MoreMicrobially induced calcium carbonate precipitation (MICP) is a biomimetic process that can be used to grow bioceramic products, such as columns and bricks, in an environmentally friendly manner. Researchers at the University of Cape Town fine-tuned the MICP process to create ceramic tiles that demonstrate mechanical properties on par with conventionally fired ceramics.
Read MoreWith the drastic increase in demand for lithium, new sources and extraction methods are needed to secure sufficient supply. Princeton University researchers led development of a new passive method for extraction of lithium from saltwater. The method, if advanced to industrial scale, could significantly decrease both the time and amount of land necessary for lithium production.
Read More