The emergence of large language models has the potential to greatly accelerate data extraction from materials science literature, but annotating the text before extraction is often still a manual task. Researchers led by Taylor Sparks at the University of Utah developed a new method that harnesses the power of Google’s Gemini Pro to reduce the need for manual annotation.
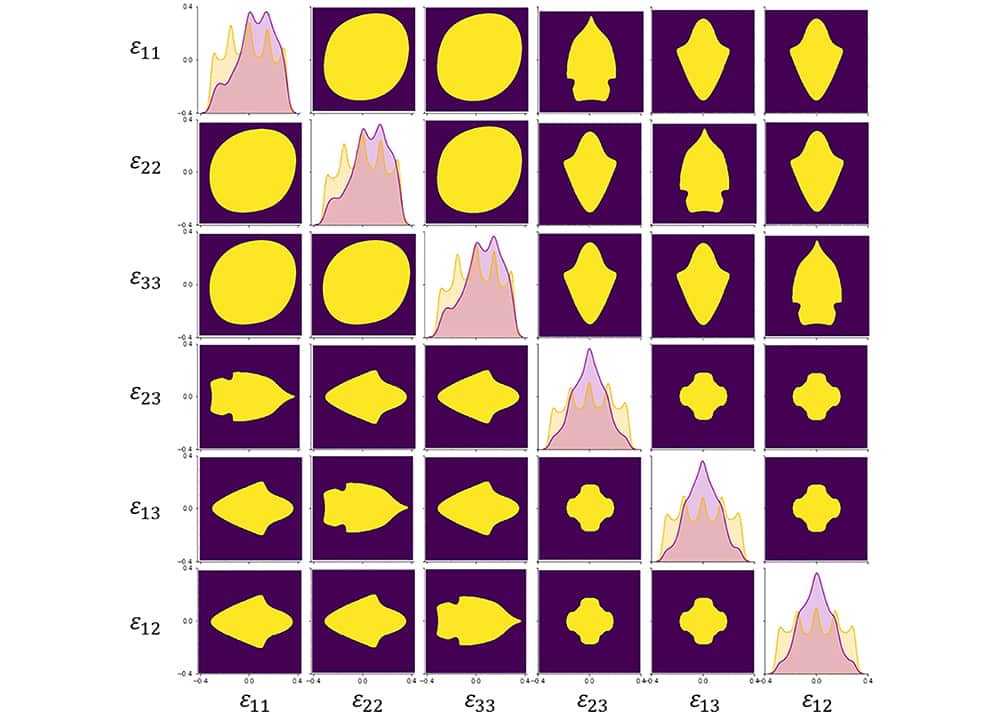
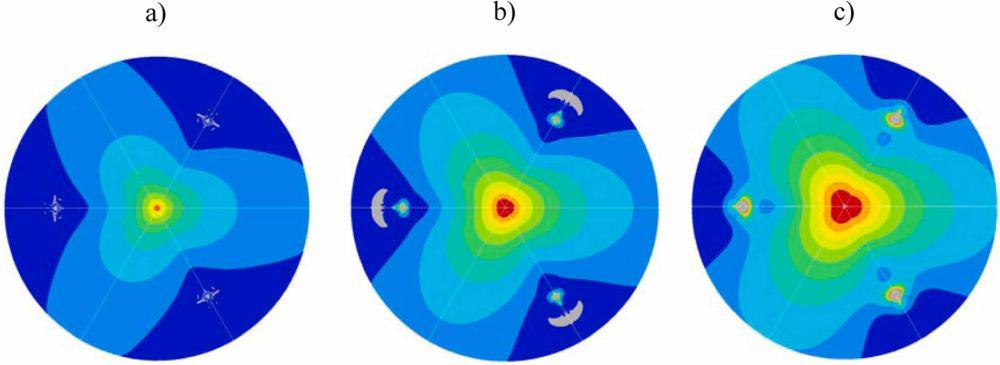
Read MoreElastic strain engineering has potential to improve processing performance in the semiconductor industry. Researchers led by Nanyang Technological University in Singapore and Massachusetts Institute of Technology used machine learning to create a map that shows how to tune the thermal and electronic properties of crystalline materials via strain engineering.
Read MoreCurrently there is no unified standard for classifying flooring materials based on their slip resistance. Researchers in Spain revealed the discrepancies between different slip tests and proposed several ways to standardize these methods to achieve more meaningful results.
Read MoreUntil now, values for the effective volume and effective surface of ball-on-three-balls test samples were only available for a small range of geometries and materials. But a new open-access paper, courtesy of researchers from the University of Leoben in Austria, provides tabulated data for a wide range of sample geometries and materials.
Read MoreThe effect niobium oxide has on the macroscopic properties of glass is reasonably well-known, but its specific structural role in glass remains poorly understood. To address this knowledge gap, researchers from the Center for Research, Technology, and Education in Vitreous Materials in Brazil combined spectroscopic data on niobium-containing silicate glasses with advanced computational modeling.
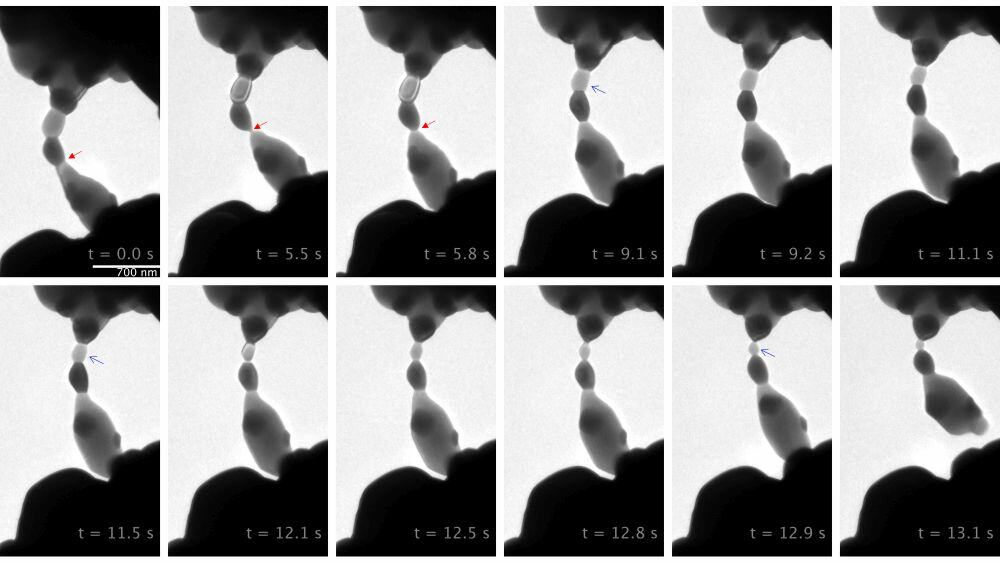
Read MoreGroup-III-nitride semiconductors have considerable potential for electronic and optoelectronic applications, but unintended defects tend to form in their structure during fabrication, which may affect the electrical properties. Two researchers at the University of British Columbia detailed the striking contrast between the effects of threading dislocation lines in gallium nitride versus indium nitride.
Read MoreWhat if you could predict a material’s internal microstructure based solely on its external surface characteristics? A new deep learning method developed at Massachusetts Institute of Technology provides such a capability, and all data and codes used for the study are freely available for anyone to use through GitHub.
Read MoreThe accuracy of models for predicting thermal properties of cemented carbides has been limited by dependance on unreliable conductivity data or time-consuming grain size measurements. Two researchers at a Sweden-based tooling company formulated a regression model that offers fairly accurate predictions using only reliable and readily measurable material characteristics.
Read MoreProcessing ceramics requires accurate knowledge of their thermal, chemical, and mechanical behaviors. In today’s CTT, ACerS Fellow Shen Dillon shares recent work he and collaborators in China and the United States published on new models for understanding sintering and creep behaviors in ceramics.
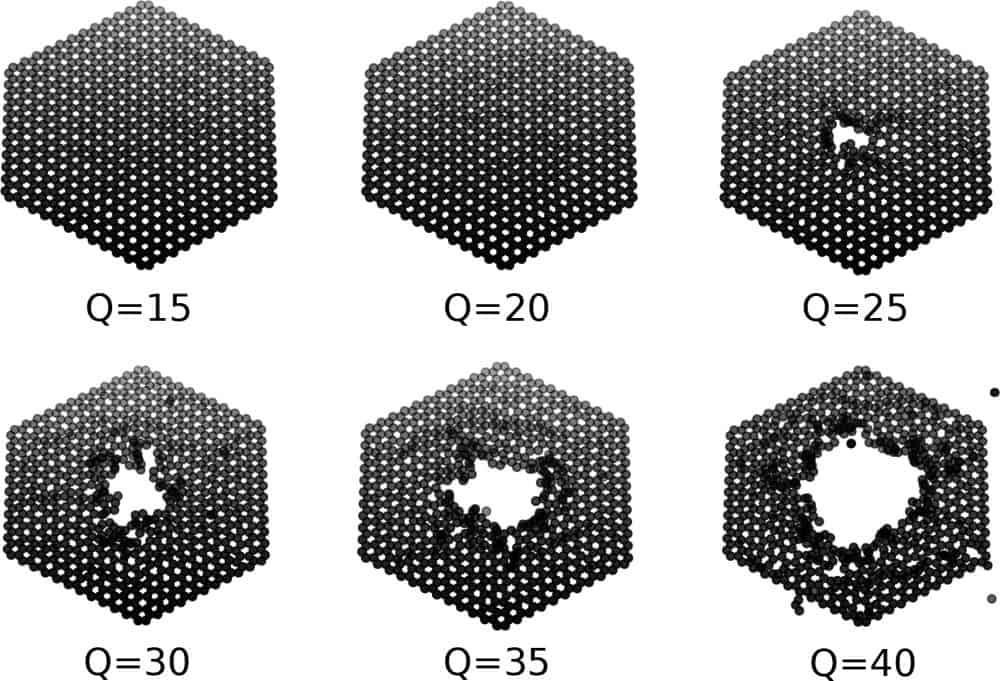
Read MoreBombarding materials with highly charged ions is one way researchers can manipulate and modify 2D heterostructures. TU Wien researchers developed a model to simulate this bombardment and reveal why, when hit, some 2D materials form nanopores and others do not.
Read More