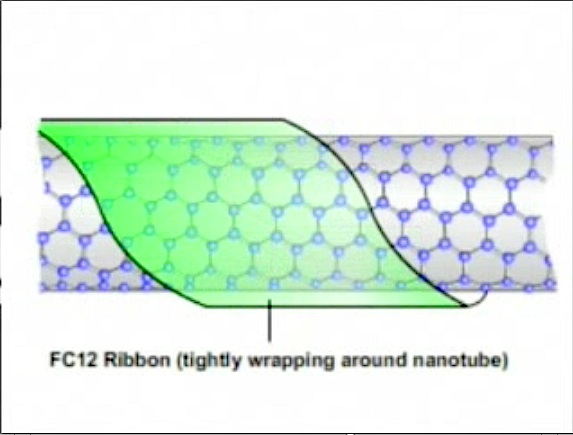
A team from UConn’s Nanomaterials Optoelectronics Lab at the Institute of Materials Science has discovered a nifty way to increase the photoluminescence of single-walled carbon nanotubes by wrapping the tubes…
Read More[flash /ceramictechtoday/wp-content/video/moving_carbon_atoms.flv mode=1 f={image=/ceramictechtoday/wp-content/video/moving_carbon_atoms.jpg}] This is a brief video. Maybe I am overwhelmed by this because of my chemistry background, but in my opinion, this video documents what truly should…
Read MorePracticing to use this “mitt” might be a little dicey, but apparently this is a serious proposal. Note, the conference referenced below is the Fifth European Conference on Space Debris…
Read MoreIn light of the previous post on the creation of platinum nanowires (as a low-cost fuel cell catalyst) via electrospinning, we stitched together an animation and several demonstrations of electrospinning…
Read MoreOne of the big divides the world of proton exchange fuel cell research is between those who are looking for an alternative to platinum (such as the University of Dayton’s…
Read MoreVia Gizmag, two Fraunhofer Institutes have teamed up to develop a clever and simple way of treating window glass to make it sensitive to motion and, thus, perfect for security…
Read MoreNIST and Johns Hopkins University researchers have unveiled a new speedy and sensitive probe that may prove to be a godsend for nano scientists and related businesses. The NIST-JHU team…
Read MoreOrganizers have announced that, due to high demand, the submission deadline for Materials Science & Technology 2009 Conference & Exhibition, slated for Oct. 25-29 in Pittsburgh, has been extended to…
Read MoreIf you want to make money in nanomaterials, the place to invest is in nano-improved intermediary products, such as coatings, memory chips, catalysts and batteries, according to a new report…
Read More