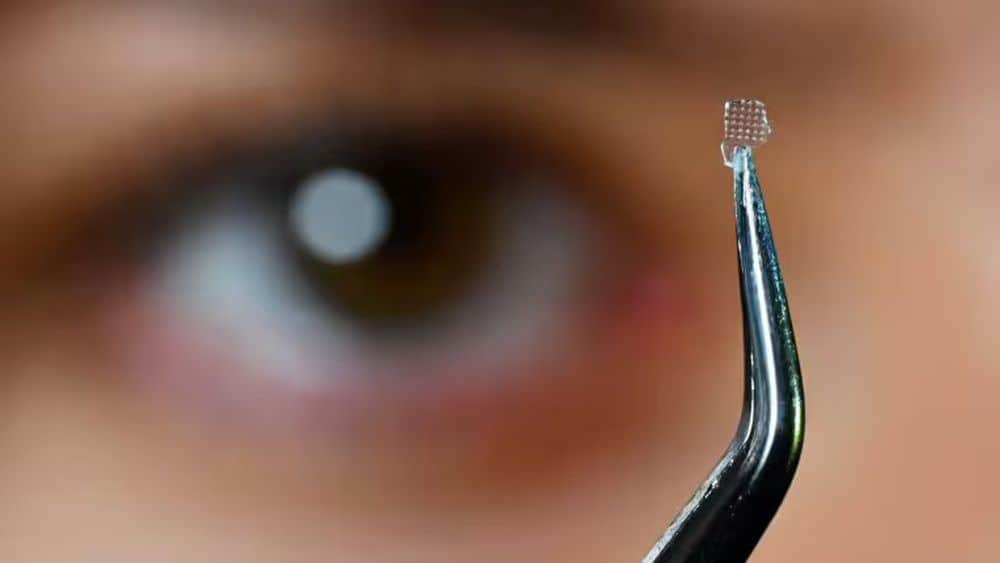
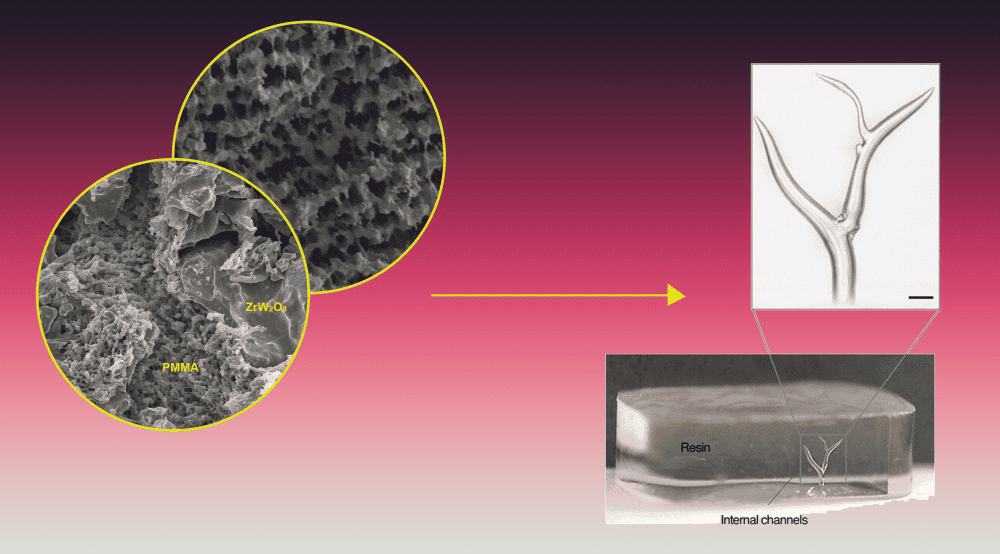
Advancements in the ceramics field have often supported innovation and discoveries in other fields. Now, knowledge gained from early work on ice-templated ceramics is aiding in the development of soft, bioinspired materials for medical applications.
Read MoreMass producing long, high-quality semiconductor fibers for use in wearable technology is challenging. Researchers at Nanyang Technological University in Singapore identified the ideal combination of materials and processing parameters to achieve consistent production of ultrathin, ultralong, high-quality semiconductor fibers using the molten-core method.
Read MorePrintable electronic inks and their associated print processes tend to rely on environmentally hazardous chemicals, which offsets the benefits of printed electronics in application. Engineers at Duke University developed a water-only printing process for fabricating printed electronics.
Read MoreEnsuring quality of nanomaterials can be difficult when producing in bulk. Rice University researchers developed a new wet-thermal etching method that can result in mass yields of up to 29% purified boron nitride nanotubes.
Read MoreIncorporating practices commonly regarded as sustainable into an individual or group’s workflow does not always guarantee environmental benefits. Researchers from the Technical University of Darmstadt published a case study that shows the importance of critically evaluating perceived green technologies before adoption.
Read MoreTheoretical studies have predicted that 2D silicon carbide in a stable honeycomb structure is possible, but experimentally achieving this material has proven difficult. Two recent papers successfully synthesized monolayer silicon carbide using top-down and bottom-up synthesis methods, respectively.
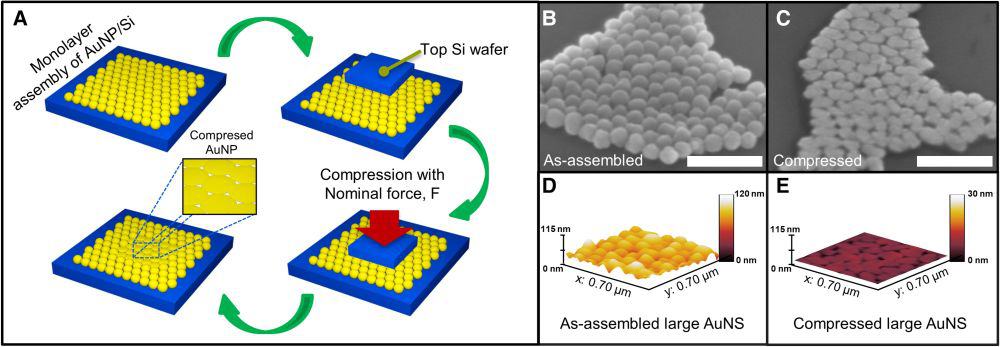
Read MoreTwo-dimensional thin films are often fabricated using bottom-up solution-based techniques, such as electrochemical deposition and atomic layer deposition. Now researchers have reported a top-down, solid-state method based on the age-old Egyptian craft of goldbeating that they say is generalizable to various metallic, polymeric, or ceramic nanoparticles.
Read MoreSeveral oxides are routinely used as sintering aids in the fabrication of zirconia toughened alumina. While the individual effects of these oxides are well recorded, the effect of multiple oxide inclusions is unclear. Researchers from several institutions in Bangladesh investigated the combined effect of these oxides on the zirconia toughened alumina system.
Read More