Though gas ovens are considered more energy efficient than electric ovens, they still face challenges with dissipation of heat into the environment. Porous volumetric ceramic burners are a combustion technology that may improve heat transfer in gas ovens, and researchers in Germany investigated the technology’s heat transfer mechanisms to better illuminate its potential.
Read MoreTransparent ceramics serve as the gain medium in many commercial lasers, yet the push to develop new and improved ceramics for this application continues. In two papers published this year, an international team of researchers investigates the influence of different processing parameters on the properties of nanocomposite yttrium magnesium oxide ceramics.
Read MoreQuality control of graphene is a pressing challenge for suppliers of the 2D material. Yet recent research at Ames Laboratory offers a valuable way to assess the quality by evaluating broad components of the diffraction pattern that scientists overlooked for years.
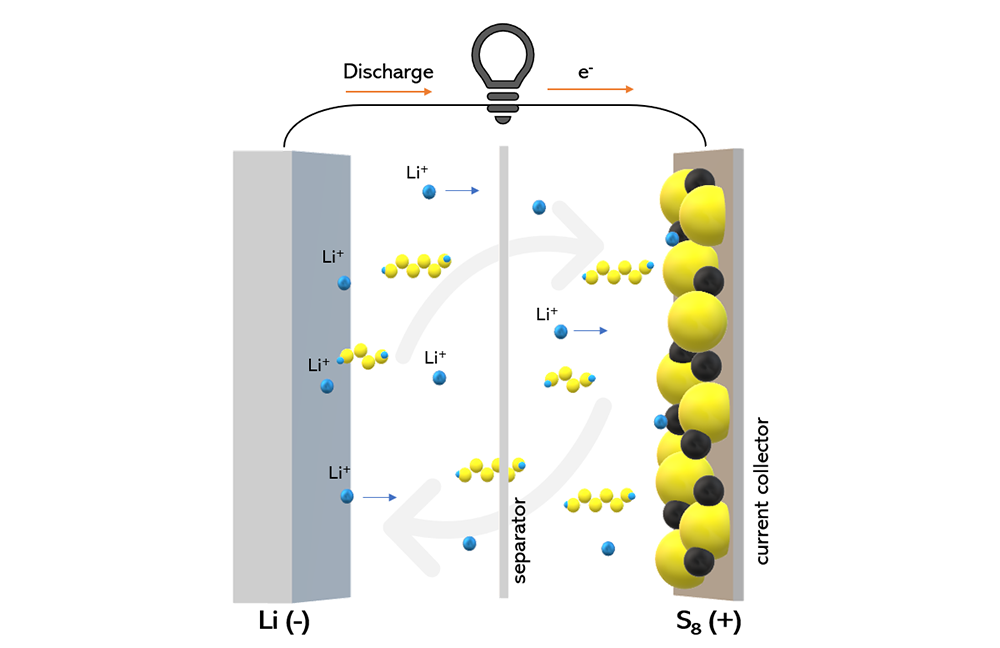
Read MoreHighly conductive carbon materials are frequently investigated as host materials for sulfur in lithium-sulfur batteries, but such cathodes struggle with loss of sulfur due to the carbon surface being nonpolar. An international team of researchers explored if using polar silica instead as the host material may improve cycling stability, even though silica is nonconductive.
Read MoreIn 2017, an international team of researchers led by the University of Cambridge found a certain alcohol-based solvent allowed uniform deposition of inks containing 2D materials—a result important to advancing printed electronics. Now, the team has proposed a mechanism to explain their finding.
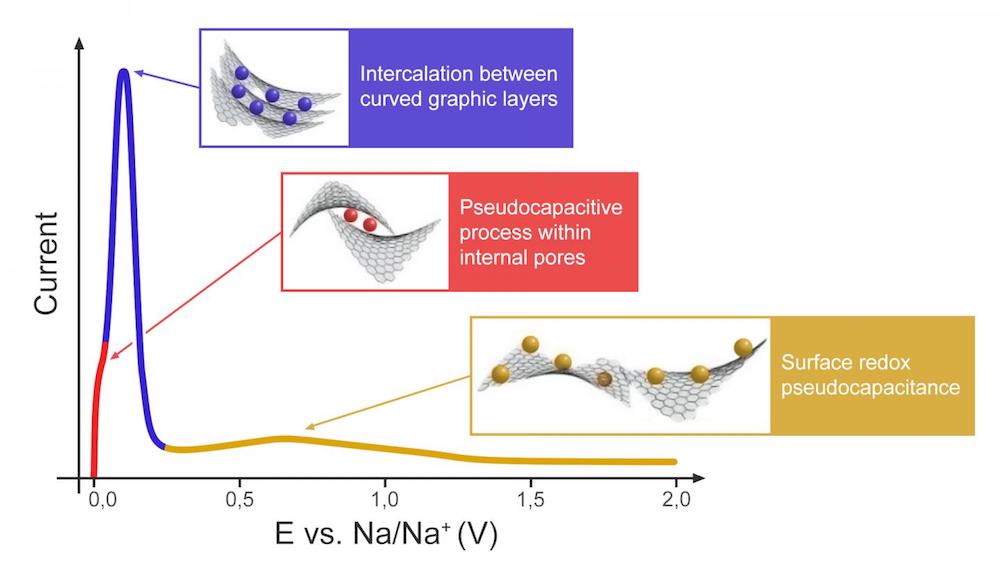
Read MoreIn developing sodium-ion batteries, hard carbon is the material most often used for the anode, but unknowns concerning the charge storage mechanism in this material hinder further development. Researchers have proposed several models to explain the charge storage mechanism, and a recent study lends support for the three-stage “adsorption-intercalation-adsorption” process.
Read MoreFast grain boundary diffusion of cations is a well understood phenomenon in metals—but much less is known about this phenomenon in oxygen-ion conducting metal oxides. Researchers at RWTH Aachen University simulated this diffusion and found that although metal ions move faster along the boundaries than in bulk, the process is not necessarily less energy intensive.
Read More